Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Power line
Induced or
displacement
current
i
d
i
d
R
1
R
1
R
2
1
r
0
V
c
=i
d
r
0
V
c
=i
d
r
0
/ (1+2R
2
/R
1
)
r
0
Fig. 3.3
Effect of PLI in ECG measurements and DRL circuit
through the patient body and right leg, which is used as reference. Considering
a small resistance r
0
of common lead wire (at right leg) and displacement
current i
d
, the small drop V
c
= r
0
i
d
appears as common to first stage of INA. A
high-CMRR INA can minimize this effect. Additionally, a driven leg circuit
(DRL) is used [
13
,
18
], as shown in Fig.
3.3
.
In DRL circuit, two sensing registers (R
1
) are used to invert, amplify, and
feedback the voltage V
c
to the right leg of the patient. The modified common-mode
voltage becomes
i
d
r
0
1
þ
2R
2
=
R
1
V
c
¼
ð
3
:
4
Þ
Hence, the interference signal is minimized at the amplifier input. An IC for
DRL circuit is described in [
19
].
2. Patient isolation: The objective of patient safety is a biosignal measurement
application to ensure that current from the acquisition circuit or its applied part
can flow through the patient body to ground, termed 'leakage current,' which
remains within safe levels in case of a fault. Thus, all biomedical amplifiers
must satisfy some safety criteria for the worst-case voltage breakdown and
maximum leakage currents through the input leads attached to the human body.
The accepted international standard is IEC-601 for Medical Electrical Equip-
ment adopted by Europe as EN-60601. This is combined with to UL (Under-
writers Laboratories Inc.) standard 2601-1 for the United States [
20
] and
endorsed by health industry manufacturers association (HEMA) and national
electrical manufacturers association (NEMA) and US Food and Drug Admin-
istration (FDA). IEC-60601-1 standard allows a patient auxiliary current
(current that can flow between two separate leads connected to the patient





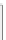

Search WWH ::

Custom Search