Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
detection. At first, the following parameters are computed for the entire dataset
using the 96-ms window, slid with a step of 20 ms:
1. Maximum QRS amplitude span in 96-ms window;
2. Maximum 8-point average positive slope (inter-sample difference).
This captures the tallest and sharpest QRS in the dataset.
The following rules for QRS neighborhood are fixed as: (1) amplitude span in
moving 96-ms window should exceed 80% of maximum amplitude span computed
over same window span. Let this value be span
th
. This rule is named as 'amplitude
threshold' criteria (ATC). (2) Average (8-point) slope should exceed 80% of
maximum average slope (say, mx_slp) computed over dataset in a moving 96
samples. Let this value be slp
th
. This rule is named as 'slope threshold' criteria
(STC).
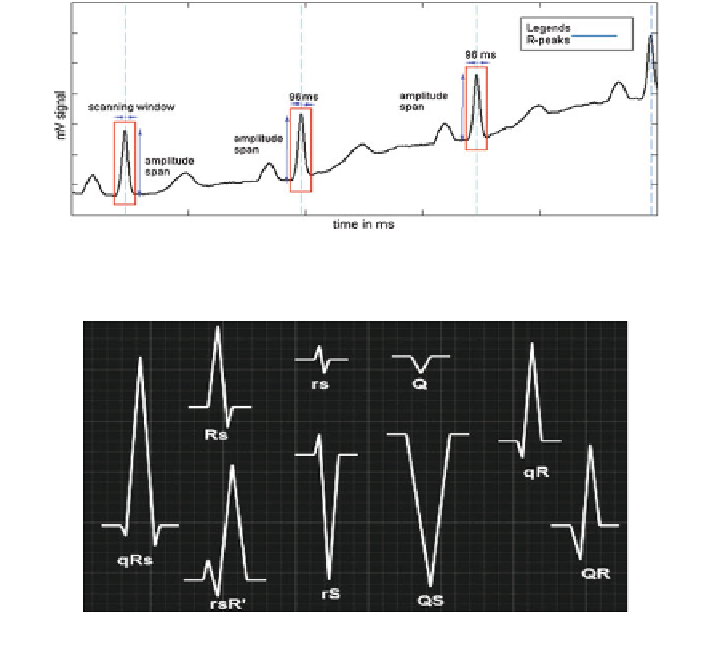
Now, from the beginning of the ECG dataset, a fresh search is initiated in a
sliding 96-ms window with step of 20 ms to meet span
th
criteria. This may locate a
probable QRS neighborhood. This is shown in Fig.
2.9
. It is also concluded that to
Fig. 2.9
QRS detection by sliding window
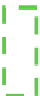
Fig. 2.10
Different QRS types captured by 96-ms window



















































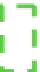































Search WWH ::

Custom Search