Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
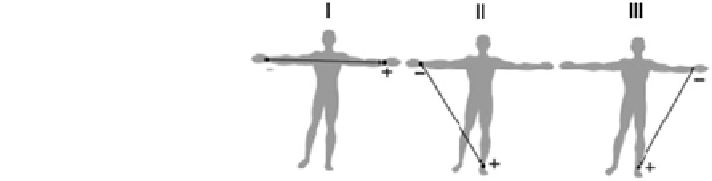
Fig. 1.5 Standard lead
positions of Einthoven
and left leg of a person standing with laterally stretched hands, which forms an
equilateral triangle with the vertices on a circle. Einthoven's bipolar leads, also
called standard leads, are defined as
Lead I
¼
V
LA
V
RA
ð
1
:
3
Þ
Lead II
¼
V
LL
V
RA
ð
1
:
4
Þ
Lead III
¼
V
LL
V
LA
ð
1
:
5
Þ
where
V
LA
: potential of the left arm.
V
RA
: potential of the right arm.
V
LL
: potential of the left leg.
The lead positions and connections for the standard leads or limb leads
developed by Einthoven are shown in Fig.
1.5
.
Later on, Frank Wilson defined and standardized unipolar leads with three
unipolar limb leads and six precordial chest leads, measured w.r.t. a reference
terminal outside the body, named Wilson central terminal (WCT). WCT is realized
as a resistive network using 5-kX resistances and given as
V
WCT
¼
1
3
ð
V
LA
þ
V
RA
þ
V
LL
Þ
ð
1
:
6
Þ
The precordial chest leads are defined as
Lead VL
¼
V
LA
V
WCT
ð
1
:
7
Þ
Lead VR
¼
V
RA
V
WCT
ð
1
:
8
Þ
Lead VF
¼
V
LL
V
WCT
ð
1
:
9
Þ
Later on, E. Goldberger modified the precordial leads to develop 'Augmented
Limb Leads,' aVR, aVL, and aVF, respectively, by opening the exploring lead
connections with the WCT. The lead connections are given in Fig.
1.6
. The lead
positions are given in Table
1.1
.
The chest leads v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, and v6 measure the cardiac potentials at
specified intercostal spaces of the chest w.r.t. WCT. These six leads define the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search