Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
4 h
24 h
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
C3-tris
4
(100 μM)
Figure 19.6
Cardiac bradycardia induced by C3-tris compared with C3 (1) and percent of control
(heart rate) was plotted for control (0.1% DMSO), C3 (1) (100 mM), C3-tris (10 mM), and 4 (100 mM) at
4 h (light gray) and 24 h (dark gray).
Control
1
(100 μM)
(10 μM)
may be useful in the treatment of Parkinson's disease as well as other CNS
degenerative disease related to neuronal apoptosis. CNS dopaminergic neurons are
particularly sensitive to the toxic effects of 6-OHDA, and we therefore tested the
ability of various fullerenes to protect from 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis of CNS
dopaminergic neurons in developing zebrafish. Dopaminergic CNS neurons are easily
identified by the presence of tyrosine hydroxylase, which can be detected by
immunohistochemistry on whole zebrafish embryos.
Fullerenes 1-4 were tested in various combinations for their ability to protect
zebrafish embryos against damage to both general CNS neurons and tyrosine
hydroxylase CNS neurons against 6-OHDA. 6-OHDA crosses the blood-brain barrier
and is taken up preferentially by dopaminergic CNS neurons, and to a lesser extent by
nondopaminergic CNS neurons. Intracellular 6-OHDA induces cellular apoptosis and
death, at least in part through oxidative injury (Silva et al., 2005). Dendrofullerene 3
showed the highest levels of general CNS neuroprotection against 6-OHDA injury,
and was able to protect 47% of total CNS neurons, while C3 (1) and 2 were
able to block 42% and 23%, respectively, of 6-OHDA-induced total CNS neuronal
death (Table 19.4). With respect to specific protection of tyrosine hydroxylase
positive dopaminergic neurons in the diencephalon, 3 (100
m
M) protected 100% of
dopaminergic neurons, while C3 (1) (100
M) each protected 60% of
dopaminergic neurons. Figure 19.7 and Table 19.5 show results obtained with 4,in
protecting CNS dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA-induced cell death.
m
M) and 4 (250
m
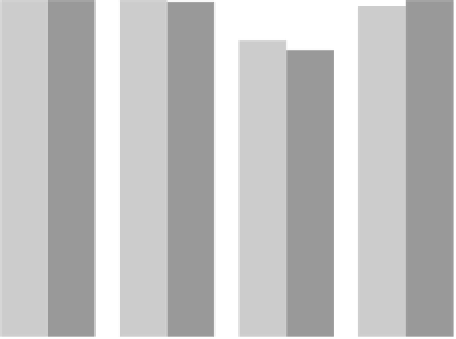

Search WWH ::

Custom Search