Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Uninjected control
KD control
MD
2 dpf
200 μm
3 dpf
midline
4 dpf
5 dpf
Sagittal section
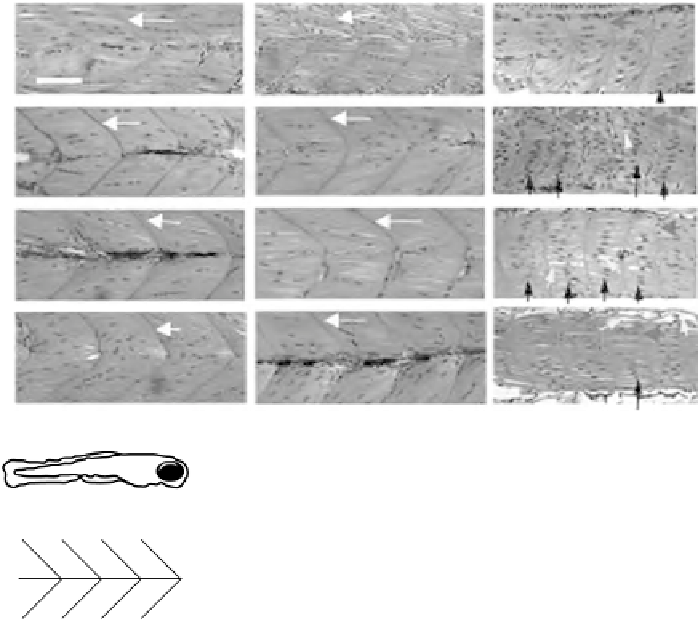
Figure 18.7
Histological assessment of muscle structure in uninjected, KD control, and MD
zebrafish. Two to 5dpf uninjected, KD control, and MD zebrafish were processed for JB-4 embedding,
sectioning, and H&E staining. Sagittal sections of tail muscles posterior to the anal pore (blue box in
cartoon in left panels) are shown at 400
magnification. Uninjected and KD control animals exhibited
normal V-shaped myotomes (white arrows) with a clear midline at the tip of the V (long black arrows),
whereasMD zebrafish exhibited short, missing, or irregular shapedmyotomes (gray black arrows), and no
discernable midline. In addition, at 3dpf, centralized nuclei (short black arrows), indicating regeneration
subsequent to necrosis, and vacuole spaces between fibers (white arrows), indicating degeneration, were
observed in most muscle fibers. In contrast, muscle fibers in control animals exhibited tightly packed, less
centralized nuclei; large vacuole spaces were not observed. White scale bar indicates 200 mm; anterior,
right. (See the color version of this figure in Color Plates section.)
reflecting regeneration; these phenotypes persisted through 4dpf. On 3 and 4dpf,
transverse myoseptum (the connective tissue separating the dorsal and ventral
myotomes) was missing inMD zebrafish. In comparison, muscle fibers and transverse
myoseptum appeared normal in KD control zebrafish. At 3 and 4dpf, MD zebrafish
exhibited 22 and 25muscle fibers/area, respectively. In contrast, KD control exhibited
8 and 7 muscle fibers/area, respectively; 2.75-fold (22/8
¼
2.75) and 3.57-fold
(25/7
¼
3.57) increase in number of muscle fibers was observed in MD zebrafish









































Search WWH ::

Custom Search