Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
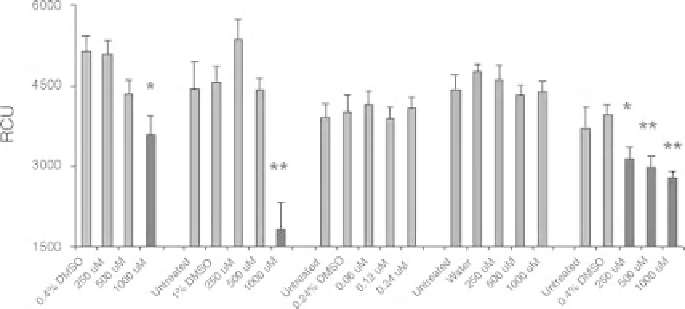
Figure 17.3
Drug effects on Xt Colo320 cells. Significantly lower chemiluminescence signal was
observed after treatment with 5-FU, oxaliplatin, and 5-FU þ leucovorin, indicating inhibition of Xt
Colo320 cell proliferation, whereas no effect was observed after treatment with camptothecin and
leucovorin. Data are presented as meanSE (
n
¼14). 0.24%, 0.4%, and 1% DMSO or water were
used as vehicle controls. Red bars indicate concentrations that caused statistically significant effects.
RCU, relative chemiluminescence units.
indicates
p
<0.05 and
indicates
p
<0.01. (See the color
version of this figure in Color Plates section.)
1000
M, LC
10
was not determined for 5-FU, oxaliplatin, and leucovorin. Based on
LC
10
estimations, three concentrations, 0.24, 0.12, and 0.06
m
m
M, were assessed for
camptothecin, and 1000, 500, and 250
m
M were assessed for oxaliplatin, leucovorin,
and 5-FU
leucovorin combination.
Test drug was added to fish water immediately after xenotransplant. After
treatment for 3 days, zebrafish were processed for Xt ELISA using survivin
antibody. For all experiments, drug-treated Xt zebrafish were compared with vehicle
control, either DMSO or fish water, and results are shown in Fig. 17.3. Significant
inhibition (
P
þ
0.05) of Xt cancer cell proliferation was observed for 5-FU (3-43%
inhibition), oxaliplatin (3-60% inhibition), and 5-FU
<
leucovorin (22-31%
inhibition), and inhibition was dose dependent, whereas significant inhibition was
not observed for camptothecin. As expected, leucovorin alone did not inhibit Xt
cancer cell proliferation; however, 5-FU
þ
þ
leucovorin combination caused
significant inhibition.
To further validate Xt ELISA, we compared cancer drug results in zebrafish with
results in humans. Overall prediction rate in Xt zebrafish was 80% (4/5) for Colo320
cells and 60% (3/5) for SW620 cells.
17.5 CONCLUSIONS
In vitro
cell lines, including the NCI-60 human cancer cell lines, are extensively used
for primary drug screening; however, results using these
invitro
assays are significantly
different from results observed in complex,
in vivo
physiological environments.
Furthermore, xenotransplant rodent cancer models are laborious, time consuming,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search