Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
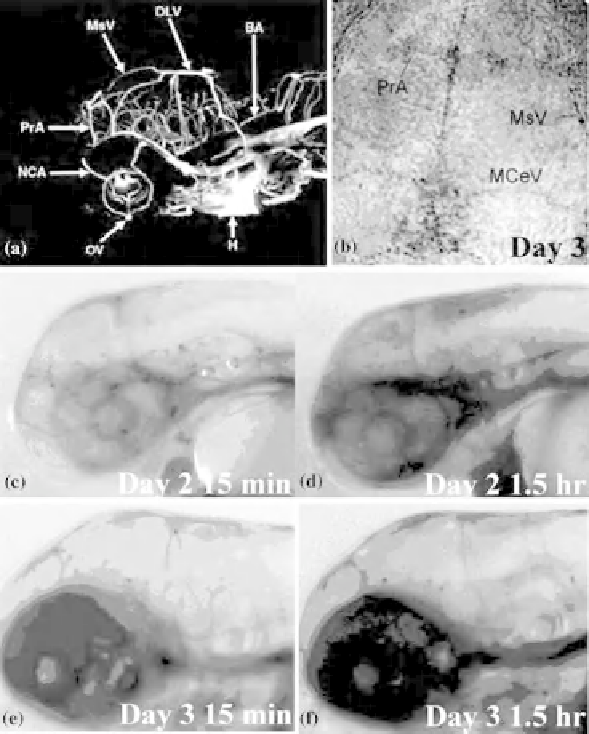
Figure 10.6
Confirmation of BBB formation in zebrafish by microangiography, antibody
staining, and dye injection. (a) After injecting dextran-rhodamine beads, microangiography was used
to image the entire brain vasculature in 3dpf zebrafish; the major brain ventricles are completely
formed, angiogenic vessels are well formed, and the blood vessel network, which transports nutrients to
brain cells, can be visualized in the brain. (b) Tight junctions are present during early development.
Whole mount ZO-1, a tight junction component, antibody immunostaining showed that tight junctions
form in the brain (brown spots) adjacent to the mesencephalic vein (MsV), middle cerebral vein
(MCeV), and prosencephalic artery (PrA) (arrows). BA, basilar artery; DLV, dorsal longitudinal
anastomotic vessel; NCA, nasal ciliary artery; OV, optic vein; H, heart. (c-f) Conventional Evans blue
dye injection method was used to confirm the presence of BBB in zebrafish. Evans blue dye was
microinjected into the peripheral blood vessels in 2 (c and d) and 3dpf (e and f) zebrafish. Distribution of
the dye was assessed in the brain at 15min (c and e) and 1.5 h (d and f) after microinjection. In 2dpf
zebrafish (c and d), Evans blue dye was observed in the brain blood vessels (arrow) at 15min (c);
however, permeation of dye to the midbrain and hindbrain regions was observed at 1.5 h (d). In contrast,
in 3dpf zebrafish (e and f), after injection, Evans blue dye was retained in the brain blood vessels at both
15min (e) and 1.5 h (f) and was not found in brain tissue, indicating the presence of BBB in 3dpf
zebrafish. (See the color version of this figure in Color Plates section.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search