Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
For the following, assume that we have an S-box whose input is
X
and output is
Y
. If we have two particular
inputs,
X
1
and
X
2
, let
Here, Ω,
X
is the differential for the two plaintexts. Similarly, for the two corresponding outputs of the above
plaintexts,
Y
1
and
Y
2
, respectively, let
To construct the differential relation, we consider all possible values of Ω
X
, and we want to measure how this
affects Ω
Y
. So, for each possible value of
X
1
and Ω
X
(and, therefore,
X
2
), we measure
Y
1
and
Y
2
to obtain Ω
Y
and
record this value in a table.
Table 7-1
shows some the results of performing this analysis on the EASY1 cipher,
with each entry being the number of times Ω
X
gave rise to Ω
Y
. (The entry in
Table 7-1
corresponding to 0
⇒
0 is
the hexadecimal value 40, meaning that it is always true. This is because no difference in the input will always,
of course, give no difference in the output.)
Table 7-1
Top-Left Portion of the EASY1 Table of Characteristic Probabilities
Note that this is only a sample of the complete table.
However, more often it is useful to collect characteristics with the highest probabilities in a list format. By
searching through the complete table of the differential analysis of the EASY1 cipher's S-box, we would note
that the two largest entries are 6 and 8, representing probabilities of 6/64 and 8/64, respectively.
Tables 7-2
and
7-3
give listings of all of the characteristics with these probabilities.
Table 7-2
S-Box Characteristics of EASY1 with a Probability of 6/64
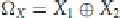
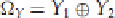

Search WWH ::

Custom Search