Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
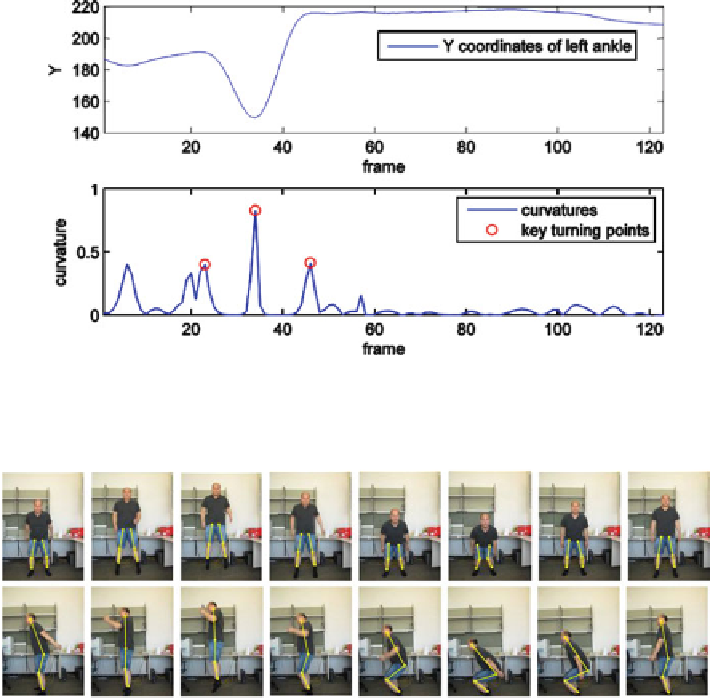
Fig. 3 An illustration of key turning point detection
Fig. 4 Key joint tracking results in anterior and lateral views. The sticks are marked with
line
segments
In testing, it was required that jumpers wear shorts so that upper legs and lower
legs have different colors. Before starting the tracking process, users need to assign
body part labels to the segmented blobs in the first frame. There is no strict
restriction on the initial poses of the jumper. All of the following steps are
automatic. Figure
4
shows an example of tracking results in different views in a
cluttered background. Note that these two videos were captured at different times.
One observation from our experiments is that
x
and
y
components of each key
joint motion have different meaning: the motion of the
y
component shows the
common features shared by different jumps even being observed from different
views, i.e., the preparing, jumping, and landing sections are well defined, while
the
x
component shows the characteristics of each specific jump. This is clearly
visible in Fig.
5
.