Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
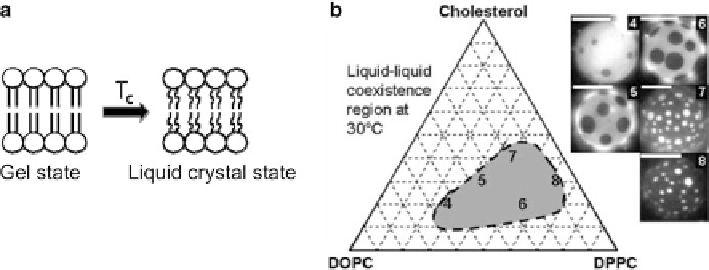
Fig. 4.3
(
a
) Schematic showing the phase transition behavior of a lipid bilayer. (
b
) Phase diagram
of the DOPC/DPPC/cholesterol tri-component mixture. The region encased by the dashed line
is liquid-liquid immiscible region. The GUVs' compositions in micrographs
4
-
8
are (
4
)2:1
DOPC/DPPC
C
20% Chol; (
5
) 1:1 DOPC/DPPC
C
30% Chol; (
6
) 1:2 DOPC/DPPC
C
20% Chol;
(
7
) 1:2 DOPC/DPPC
C
40% Chol; and (
8
) 1:9 DOPC/DPPC
C
30% Chol. Scale bars are 20
m
(Reprinted with permission from Ref. [
18
]. Copyright 2003, Biophysical Society)
DPPC is the most permeable at
41
ı
C, while DOPC can retain its content for a
long time at room temperature. At T
c
, lipid packing is constantly changing back
and forth from the gel state to the liquid crystal or crystalline state, rendering a
high permeability. Cholesterol is a special lipid, whose polar head group is just a
hydroxyl. Cholesterol has a significant influence on the T
c
[
14
]. For high-T
c
lipids
such as DPPC, cholesterol disrupts lipid packing and results in lowering the T
c
making the liposome more liquid-like. The addition of cholesterol to fluid DOPC
increases liposome elasticity, allowing the liposome to behave as if in a gel-like
state [
15
,
16
].
In cases where the liposome is made up of a mixture of both high- and low-
T
c
lipids, lateral phase segregation or domain formation may take place. For
example, saturated lipid tails with more than four methylene unit differences
result in nonideal mixing leading to lateral phase separation. If the difference
is only two methylene units, the lipids are usually completely miscible [
17
].
A commonly used lipid mixture to achieve lateral phase separation has been
identified as DOPC/DPPC/cholesterol. Certain dyes are selectively dissolved only
in one of the domains, allowing the observation of lipid phase separation using
fluorescence microscopy. For example, by increasing the percentage of DPPC, the
area of the stained domains is significantly reduced (Fig.
4.3
b), where Texas Red
dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine prefers the less ordered DOPC phase [
18
].
Domain formation has become an increasingly important topic in biophysics for
better understanding cell membrane behaviors. Its applications in nanotechnology,
however, have not been widely explored.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search