Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
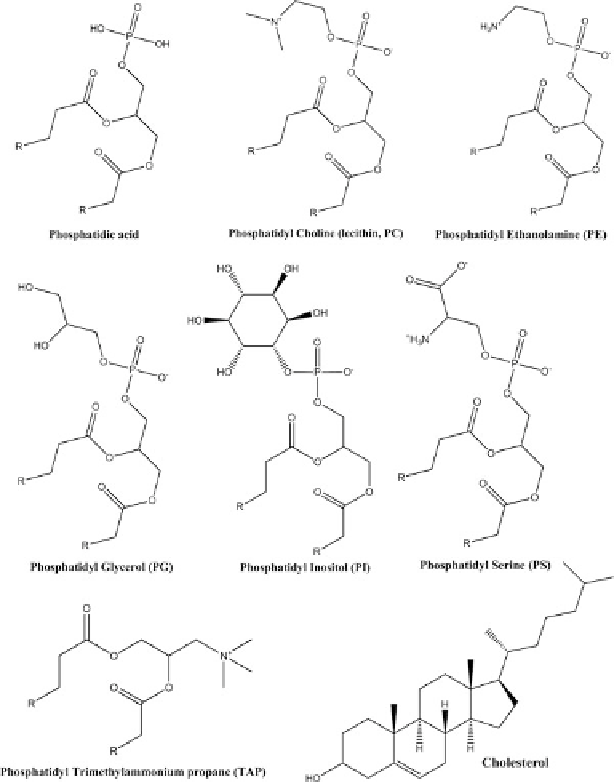
Fig. 4.2
The general types of phospholipids and cholesterol typically used to make liposomes
scanning calorimetry (DSC), T
c
can be precisely determined. T
c
is a function of
the acyl chain length. For example, lipids such as DOPC have a double bond in the
hydrophobic tail, forming a kink and preventing efficient packing of the lipids tails
resulting in a low T
c
value of
20
ı
C. On the other hand, DPPC has no kinks and
can pack better resulting in a high T
c
of 41
ı
C. In general, the T
c
value decreases
considerably in the presence of unsaturated acyl chains, branched chains, or bulky
side groups.
The lipid bilayer is hydrophobic and thus inhibits the passage of polar and
charged compounds into the liposome. Permeability of the bilayer membrane is a
function of temperature and is the highest around the T
c
of the lipid. For example,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search