Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Scheme 3.7
Synthesis of 4-Se-thymidine phosphoramidite, DNAs. (
a
) TMS-Im and MeCN. (
b
)
1H-triazole, POCl
3
,Et
3
N. (
c
) (NCCH
2
CH
2
Se)
2
,NaBH
4
, EtOH. (
d
) 10% Et
3
N in MeOH. (
e
)2-
Cyanoethyl N,N-diisopropyl(chloro)phosphoramidite and EtN(i-Pr)
2
in CH
2
Cl
2
.(
f
) Solid-phase
synthesis
3.4.2
Selenium Modification on Nucleobase
3.4.2.1
4-Selenothymidine
Chemical synthesis of 4-selenothymidine-containing DNAs was achieved in 2007
by Huang's lab [
76
]. The synthesis was accomplished by activating 4-position
with 1H-triazol-1yl, followed by the substitution using cyanoethyl selenide [
77
]
(Scheme
3.7
). The selenium reagent (dicyanoethyl diselenide) was specifically
developed for this transformation, and it can be reduced to cyanoethyl selenide,
a very strong nucleophile for the selenium functionalization. The incorporated
selenium functionality is partially protected with cyanoethyl group [
77
], which can
be removed under a weakly basic condition after the oligonucleotide synthesis.
Since “Huang” means yellow in Chinese, thus, this useful yellow diselenide
reagent is also called Huang Reagent. Detailed synthesis protocol is available in
Current Protocols in Nucleic Acid Chemistry [
78
]. Thermal denaturing experiment
suggested that the 4-Se-T-DNA duplex has the similar melting temperature and
duplex stability as the native one [
76
].
Our X-ray crystallographic data also showed no obvious structure change when
compared to the native one (Fig.
3.5
a, b). The local structure of the Se modification
site (Fig.
3.5
c) indicates that the thymidine 4-Se atom forms a hydrogen bond with
adenosine N6-H on the complimentary strand. The Se-modified base is shifted by
0.4 A to accommodate the large selenium atom.





























































































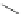



































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search