Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
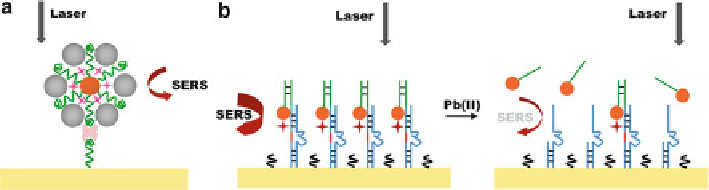
Fig. 13.6
(
a
) Schematic illustration of SERS-based sensor for thrombin detection by using
aptamer-modified AuNPs. (
b
) Schematic of SERS-based sensor for detection of Pb
2C
by using
DNAzyme modified AuNPs
13.2.3
AuNP-Based SERS Sensor
Raman spectroscopy is a laser-based optical technique used to analyze molecular
structure information such as molecular bonds, conformations, and intermolec-
ular interactions. However, Raman scattering is inherently weak and inefficient
(10
-30
cm
2
per molecule vs. 10
-16
cm
2
per molecule for fluorescence), and as a result
the main challenge of Raman spectroscopy is producing a highly sensitive signal for
sensor application [
76
]. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy or surface-enhanced
Raman scattering (SERS) is a much more sensitive technique that enhances Raman
scattering of molecules adsorbed on the surface of certain nanostructured metals
(e.g., gold and silver) [
77
]. These large enhancements result predominantly from the
extremely high electromagnetic fields produced on hot spots by the surface plasmon
excitation of the free electrons in metal nanostructures [
78
]. The sensitivity of SERS
hasbeenshowntobeashighas10
14
-10
15
, suggesting the possibility of developing
ultrasensitive chemical and biological sensing methods on SERS [
79
]. This has
several advantages over fluorescence as it can provide spectral fingerprinting
information of molecules, does not suffer from photobleaching, and has narrow line
width of vibrational Raman bands, which could be used for multiplexed detections.
By labeling gold nanoparticles with oligonucleotides and Raman-active dyes,
Mirkin and coworkers first reported a SERS-based sensor for DNA detection with
a 20 femtomolar detection limit [
4
]. From then on, numerous SERS-based sensors
have been performed for DNA detection [
80
-
85
]. To detect analytes beyond DNA,
Dong and coworkers reported a SERS sensor for thrombin detection using aptamer-
modified AuNPs (Fig.
13.6
a) [
86
]. Since
-thrombin could bind two different
DNA aptamers with high affinity, the substrate modified with aptamer 1 would
capture AuNPs functionalized with aptamer 2 and Raman reporters in the presence
of thrombin. After Ag NP deposition, the NPs became larger, resulting in an
enhanced SERS signal. The aptasensor shows high sensitivity and selectivity with
the detection limit of 0.5 nM. Base on a similar principle, a SERS aptasensor
for detection of thrombin was also reported by taking advantage of the strong
electromagnetic coupling resonance at the gold nanorod-nanoparticle junctions [
87
].
'
Search WWH ::

Custom Search