Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
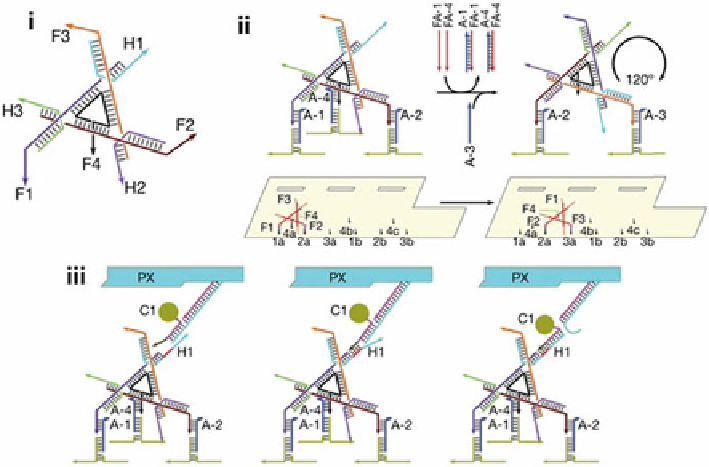
Fig. 11.17
Assembly and transportation of nanoscale objects by DNA mechanical devices. The
molecular assembly line. (
i
) The construct of the walking element, including three hands (H1-H3)
and four feet (F1-F4). (
ii
) Walking reactions (
upper images
): one stride of the walking element
requires the sequential addition of two fuel strands and on anchor strand (walker rotated by 120
ı
).
Movement of the walking element on the DNA origami track showing the interaction between
the feet and the binding sites. (
iii
) Transfer of gold nanoparticle from the machine to the walking
element (Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Ref. [
96
], copyright 2010)
been enabled to transport a molecule and to create new molecule at each step
autonomously [
82
]. In a very recent research, the group of Seeman has constructed
a robot-like DNA machine to assemble cargos as it moves (Fig.
11.17
)[
96
]. The
assembly line is implemented by the combination of three DNA-based components:
a DNA origami tile, providing the framework and also the track for the assembly
process; three DNA machines, or cassettes, serving as programmable cargo-
donating devices; and a DNA walker, moving along the track to collect and carry the
DNA cargo. The walker is fueled by single-stranded DNA that guides the walking
element to move passing by an “assembly line” of three DNA-made loading devices,
each containing a cargo, that is, gold nanoparticle. Each loading device can be
programmed to either donate its cargo to the passing walker (“ON” state) or be in
“OFF” state, where no transfer occurred, such that the walker could be controlled to
receive anywhere from zero to three particles along its
200 nm journey, to fabricate
eight different products obtained with three two-state devices. AFM was used to
visualize the process.
The mechanics of DNA hybridization was also used to transport nanosized
objects by Gaub et al. [
97
]. However, different from the previous machines made
out of pure DNA, the realization of the device reported by them is highly dependent
Search WWH ::

Custom Search