Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
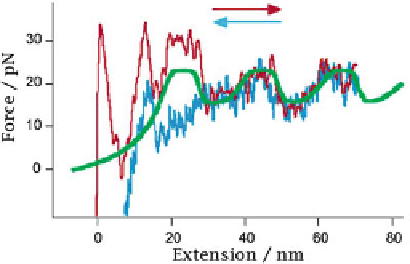
Fig. 6.21
Unzipping force
curves of complementary
oligomer ssDNA chains and
the force curve by simulations
(
smooth curve
) (Reprinted
with permission from Ref.
[
52
]. Copyright 2003
American Chemical Society)
6.4.4.1
The Binding Force in the Unzipping Mode Stretching
In 1997, Essevaz-Roulet et al. studied the binding force of two complementary
ssDNA chains. They found that a force of 10-15 pN is needed to unzip the duplex
[
51
]. In addition, this unzipping force is independent on the stretching velocity in
the range of 20-800 nm/s, which indicates that the experiments were carried out in
a quasi-equilibrium state.
In 1999, Rief et al. studied the force spectroscopy of poly(dA-dT) and poly(dC-
dG) [
31
]. The melting process was not observed for poly(dA-dT), based on which
they speculated that the binding force between A and T is stronger than that
between C and G. After melting, the special DNA formed hairpin structure when
the stretching force was lowered. By unzipping the hairpin structure, they observed
that the binding force between C and G is 20
˙
3 pN while that between A and T is
only 9
˙
3pN[
31
]. This result is reasonable because that there are triple H-bonds
between C and G but only double H-bonds between A and T.
In 2003, Gaub et al. investigated the unzipping process of a special
sequence, [dG10dA10dG10dA10dG10dA10dG10dA10dG10]. [dC10dT10dC10dT
10dC10dT10dC10dT10dC10] [
52
]. A periodic wavelike force curve was obtained,
in which the wave crest corresponds to the binding force between dC10 and dG10,
while the wave trough corresponds to the binding force between dA10 and dT10
(see Fig.
6.21
). The difference between the crest and trough is 5 - 10 pN, with a
period of 20 - 25 nm. The wavelike force curves were supported by the simulations.
6.4.4.2
The Binding Force in the Shear Mode Stretching
In 1999, Strunz et al. studied the binding force between the complementary ssDNA
chains by shear mode with 5
0
-5
0
end stretching [
53
]. They found that the binding
force is dependent on the chain length: the longer chain, the higher binding force.
For the case of 30 bp, the binding force is 48
˙
2 pN, which is significantly higher
than that measured in the unzipping mode. It was also observed that the shear
binding force is dependent on the stretching velocity: the higher stretching velocity,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search