Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 6.12
Fitting curve
of FJC model and the
experimental force curve
of ssDNA obtained in organic
solvent
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
ssDNA in DEBenzene
l
k
= 0.154 nm
l
k
= 1.0 nm
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
Normalized extension,
R / L
0
5
X
n
.LŒF =L
0
1/
n
F
D
1
D
8:44
nN
;
2
D
29:5
nN
;
5
D
1
9,637 nN
nD1
(6.6)
It is worth noting that in the studies before 2005, only linear elasticity was
considered in the curve fitting for ssDNA. When Eqs.
6.6
and
6.1
are combined
together, Eq.
6.7
can be obtained as below:
R=L
0
D
.LŒF =L
0
/
f
coth
Œ.F
l
k
/=.k
B
T/
.k
B
T/=.F
l
k
/
g
(6.7)
One should also keep in mind that water is a very complicated solvent. With
hydrogen-bonding donor and acceptor, this polar solvent strongly influences the
properties of ssDNA. The interactions between the apolar organic solvent molecules
and the solute molecules are van der Waals interactions in general, which should
be the weakest intermolecular interactions. In this condition, it is to be expected
that the solute molecules' behavior is close to that in the vacuum condition. To
avoid complicated intramolecular structures such as hairpins and loops, Cui et al.
chose an oligomer ssDNA only containing random sequence of 1:1 thymine (T)
and cytosine (C) and obtained the single-chain force curves in organic solvents (see
Fig.
6.12
[
33
]). The force curves obtained in diethylbenzene and 1-propanol can be
superimposed well, indicating that the organic solvents are a class of environment,
in which ssDNA presents the “pure” elasticity upon stretching [
33
].
The strength of a typical covalent bond can be used as the upper limit for the
stretching force, for example, 2,000 pN [
34
]. Thus, the upper limit for
L
[
F
]
/L
0
is
about 1.12, according to Eq.
6.6
. When the chain is not stretched by an external
force,
L
[
F
]
/L
0
D
1. Upon force stretching, the value of
L
[
F
]
/L
0
will increase
gradually from 1 to 1.12. In the range from 1 to 1.12, any arbitrary value of
L
[
F
]
/L
0
is reasonable and corresponds to a mapping value of
F
in the force curve, which can
be calculated with Eq.
6.6
.





































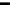





Search WWH ::

Custom Search