Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 2.9
Displacement sensor comparison by detection method
Type
Eddy current
Optical
Ultrasonic
wave
Laser focus
Contact
Detectable object
Metal
Most
objects
Most
objects
Most
objects
Solids
Detecting distance
Short
Normal
Long
Short
Short
Accuracy
High
High
Low
High
High
Response speed
Fast
Fast
Slow
Normal
Slow
Environmental
resistance
Highly
durable
Normal
Normal
Normal
Highly
durable
Detecting point
Normal
Small
Large
Small
Small
Units In the region of 0.00001 in. or 0.001 lm minimum
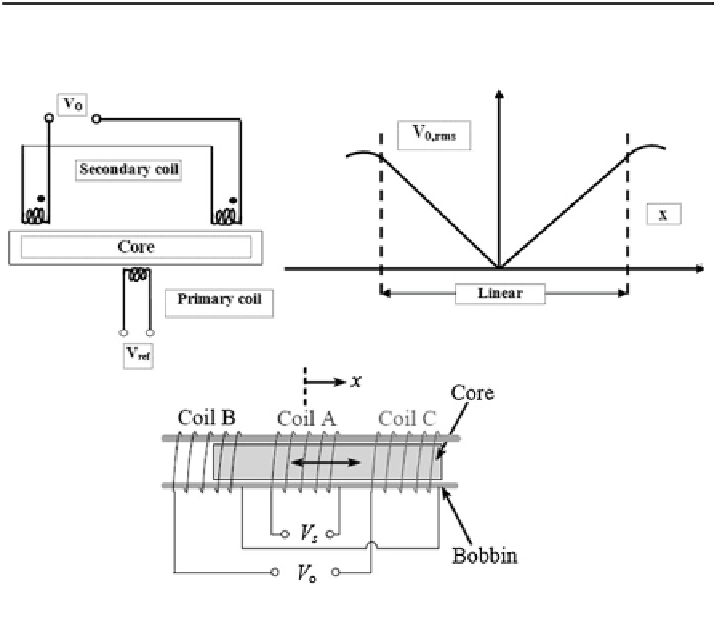
Fig. 2.13
LVDT and its characteristics
coil. In operation, the LVDT's primary winding is energized by alternating current
of
appropriate
amplitude
and
frequency,
known
as
the
primary
excitation.
Figure
2.13
shows the basic principle of LVDT and its characteristic.
The LVDT's electrical output signal is the differential AC voltage between the
two secondary windings, which varies with the axial position of the core within the
LVDT coil. Usually this AC output voltage is converted by suitable electronic
circuitry to high level DC voltage or current that is more convenient to use.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search