Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
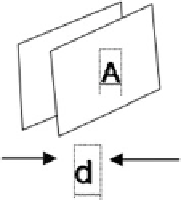
Fig. 1.8
Parallel Plate
moisture meter, and the capacitive hygrometer. Capacitance is measured in units
of Farads (F).
Capacitance measurement is suitable for measuring the level of nonconductive,
i.e., dielectric liquids like oils, gasoline, or liquid gases for corrosive acids and in
high pressure processes.
Capacitive sensors have a wide variety of uses. Some are:
• Flow-Many types of flow meters convert flow to pressure or displacement, using
an orifice for volume flow or Coriolis Effect force for mass flow. Capacitive
sensors can then measure the displacement.
• Pressure-A diaphragm with stable deflection properties can measure pressure
with a spacing-sensitive detector.
• Liquid level-capacitive liquid level detectors sense the liquid level in a reservoir
by measuring changes in capacitance between conducting plates which are
immersed in the liquid, or applied to the outside of a nonconducting tank.
• Spacing-If a metal object is near a capacitor electrode, the mutual capacitance is
a very sensitive measure of spacing.
• A capacitive type sensor is placed on bed to record respiratory movements from
the lungs and ballistrographic movements from the heart. Capacitors formed by
placing mica insulators between corrugated metal layers can be used to measure
pressure between the foot and shoe.
1.9.13 Frequency Measurement
An important electrical quantity with no equivalent in DC circuits is frequency.
Frequency measurement is very essential in many applications of alternating
current, particularly in AC power systems designed to run efficiently at one fre-
quency only. If an electromechanical alternator is generating the AC, the fre-
quency will be directly proportional to the shaft speed of the machine, and
frequency could be measured simply by measuring the speed of the shaft. If
frequency needs to be measured at some distance from the alternator, though other
means of measurement will be necessary.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search