Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
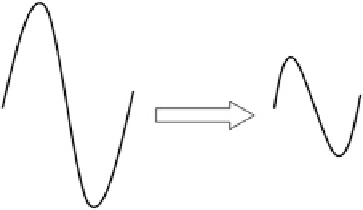
Fig. 7.2
Attenuation of
signal
Filtering
To reject unwanted noise within a certain frequency range, signal conditioners
can include filters. A further common use of filters is to prevent signal aliasing—a
phenomenon that arises when a signal is undersampled (sampled too slowly).
Isolation
Improper grounding of the system is one of the most common problems which
include noise and cause damage to measurement devices. Signal conditioners with
isolation can help to prevent most of these problems. Isolation functions include:
breaking of ground loops, rejection of high common-mode voltages, and protec-
tion of expensive instruments. Optical, Magnetic, and capacitive isolators are used
for circuit isolation and these devices pass the signal from its source to the
measurement device without a physical connection. Signal is modulated by using
magnetic and capacitive type isolators from a voltage to a frequency. Before
converting back to a voltage value the frequency can be transmitted across a
transformer or capacitor without direct physical connection.
Multiplexing
A basic method used for measuring various signals with a single ADC is
multiplexing. The ADC functions alike: it samples one channel, toggles to next
channel and samples it, and so on. As the same ADC is sampling many channels
rather than only one, the efficiency rate of each individual channel is proportional
to the number of channels sampled. The digitizer is the most expensive part of a
data acquisition system. By use of multiplexing, it can sequentially route a number
of signals into a single digitizer, thus achieving a cost-effective way to greatly
expand the signal count of system. Signal conditioners set with signal multiplexers
can cost-effectively expand the input/output (I/O) capabilities.
Digital Signal Conditioning
Digital signals can require signal conditioning peripherals.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search