Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
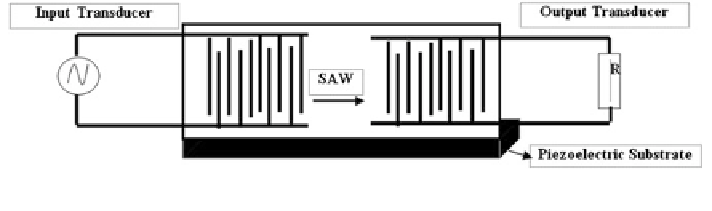
Fig. 6.22
SAW sensor
continuous upgradability in performance through increase in operation frequency,
variation
in
device
design,
development
in
polymer
interfaces,
and
planner
technology.
Advantages:
• High sensitivity and fast response times.
• Fabrication is easy.
• Diverse sensor coatings.
• Small.
• Inexpensive.
• Sensitive to virtually all gases.
Disadvantages:
• Poor signal-to-noise performance because of the requirement of high frequen-
cies to operate.
• Required circuit for operation is expensive and complex.
• Reproducibility is difficult to achieve.
• Complex circuitry.
• Temperature and humidity sensitive.
• Specificity to analyte groups affected by polymeric-film sensor coating.
Applications:
• Analysis of dairy products, perfumes, and alcoholic beverages
• Environmental analysis.
• Medical diagnosis.
6.12 Advanced Sensors
Multisensor systems implemented in E-nose are the advanced sensing devices
designed to analyze complex analytes mixtures. In the last few years, new chal-
lenges have emerged in sensor market, in particular a growing demand for
chemical sensors adaptable to nonplanar surfaces, weightless, inexpensive, and
Search WWH ::

Custom Search