Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.6
(continued)
Compound
Odor index
Methylacetate
1,100
Methylamine
940,000
Methylamylalcohol
12,650
Methylchloride
200,000
Phenol
16
Propane
425
Propionic acid
112,300
Skatole
30,000
Toluene
720
Valeric acid
256,300
• Cost and Benefit of Analysis—What is the total cost of running the instrument
including
maintenance,
methods
development,
sample
handling,
operator
training, and disposables?
Applications of odor measurement in industries
• Foods: Assessment of freshness, quality control of foods, and beverages
• Chemicals: Quality monitoring of synthetic chemicals
• Odor abatement facilities: Efficiency check of deodorizing facilities
• Deodorants: Deodorizing efficiencies
• Air cleaners: Efficiencies of deodorization
• Air conditioners: Measurements of malodors from air conditioners
• Refrigerators: Deodorizing system of offensive odors in a refrigerator
• Vacuum cleaners: Treatments for bad smell of exhaust air
• Automobiles: Odors in a new or old cabin, malodors from stuff.
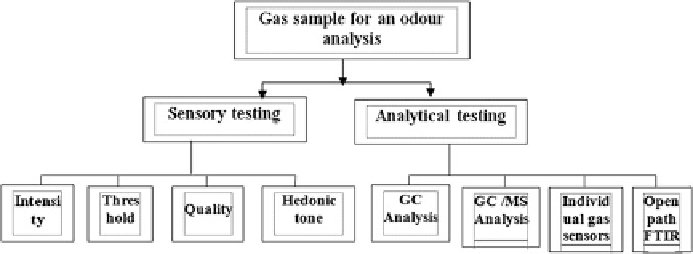
Odor evaluation methods could be categorized from various standpoints.
Figure
4.9
shows same and also Table
4.7
categorized odor measurement tech-
nology with remarkable advantages and disadvantages.
The sense of odor involves three principal factors: concentration of odorous
substances, sensory odor intensity, and odor quality including hedonic tone.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search