Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fiber output
Scutching
(fiber top)
Scutching
(fiber bottom)
Stalk breaking
Bale opening
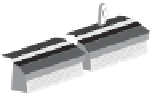
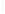
Figure 12.5
Flax scutching line. (Courtesy of Van Dommele Engineering.)
Figure 12.5, the scutching is performed by a turbine with its axis along the fiber moving
direction. There are two scutching steps. In the first step, two turbines are used for scutching
bast fiber bottoms. The second scutching step uses two other turbines to beat on bast fiber
tops. The removed trash particles and short fiber are transported to a collecting unit through
funnels and a pneumatic transportation system. Some scutching lines use a cylinder to
perform scutching process. Bast fiber layer, with a fiber-laying orientation perpendicular to
its moving direction, is moved by feeding rolls into a scutching area, where the bast fiber is
beaten by the spring steel blades mounted on the surface of a rotating cylinder to scrape off
woody core particles and short fiber (called tow fiber). In this case, the cylinder axis is parallel
to the fiber-laying orientation. Two scutching units are needed, one for rough scutching and
another for fine scutching. Additionally, this cylinder scutching is often followed by a
separating unit. This unit is composed of shaking screens that shake up fiber bundles and let
loose shives and short fiber fall into an vacuum chamber underneath the shaking screens.
Thus, clean bast fiber with shorter stalk length is produced. This line fiber product can be
packed and stored directly, or can be cut and baled by an automatic hydraulic baling press.
Another technology is a decorticating line, which produces short staple bast fiber, woody
core, and seed. Figure 12.6 exhibits the major components that constitute this bale-to-bale
fiber processing line (Temafa GmbH, 2005). In comparison with the above scutching line,
these critical components include bale opening, stalk breaking, fiber breaking and separating,
fiber opening and cleaning and bale press. After a fiber stalk bale is delivered to the feeding
point of this line, the bale is opened and fiber stalk is spread out on a moving belt to form a
continuous layer using an opener and divider. Because the decorticating line is designed for
short staple fiber production, fiber stalk laid on the moving belt does not necessarily keep
parallel. The fiber stalk breaking unit uses a large-size cylinder surfaced with scattered
beaters to crush the woody core inside the fiber. Two stalk breaking units can be arranged to
achieve a better efficiency of woody core breaking. The crushed fiber stalk is fed through
retaining rollers to a fiber breaking and separating unit to break fiber bundles and small size
shives. This is performed by a set of crushing rollers. To separate the crushed shives from
fiber bundles, horizontal or angled shaking screens are used for removing short fiber and
shives during the transportation of fiber bundles.


































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































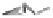


















































































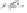









































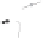








































































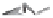


























































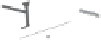























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search