Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
HO
O
HO
O
HO
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
H
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
3
C
O
H
H
CH
3
H
3
C
H
H
H
3
C
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
Lovastatin
Mevastatin
Simvastatin
HO
HO
CO
2
-
CO
2
-
HO
OH
CO
2
-
OH
OH
O
CH
3
F
CH
3
F
O
N
H
3
C
H
3
C
H
CH
3
CH
3
N
CH
3
CH
3
CONH
HO
Pravastatin
Fluvastatin
Atorvastatin
HO
HO
HO
CO
2
-
CO
2
-
CO
2
-
OH
OH
OH
F
F
F
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
CO
N
N
N
N
H
3
C
N
OO
Si
H
3
C
CH
3
CH
3
Cerivastatin
Pitavastatin
Rosuvastatin
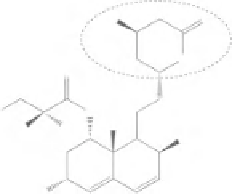
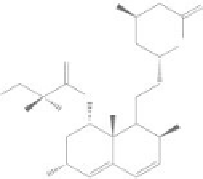
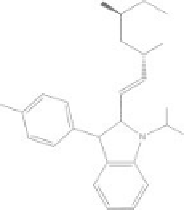
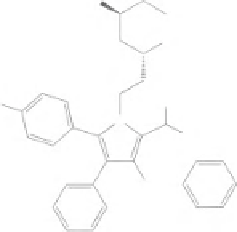
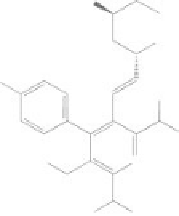
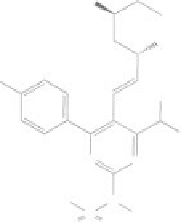
Figure 8.2
Chemical structures of statins. HMG-CoA analog is highlighted with a dashed circle.
Lovastatin and mevastatin are natural statins of fungal origin. Simvastatin and pravastatin are chemically
modified derivatives of lovastatin and mevastatin, respectively. Fluvastatin, atorvastatin, cerivastatin
(withdrawn from clinical use in 2001), pitavastatin and rosuvastatin are fully synthetic compounds
(Schachter, 2005).
growth and development but are thought to confer a selective advantage to the organism that
produces them. Well-known fungal secondary metabolites with pharmaceutical applications
include penicillin, cyclosporins, ergot alkaloids and statins.
Aspergillus
-derived statins are an excellent example of fungal secondary metabolites that
have made a great impact to human health as a drug. Statins are widely used for reducing
plasma concentrations of total and LDL cholesterol in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia
and reducing the risk of heart attacks. Statins are hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme









Search WWH ::

Custom Search