Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
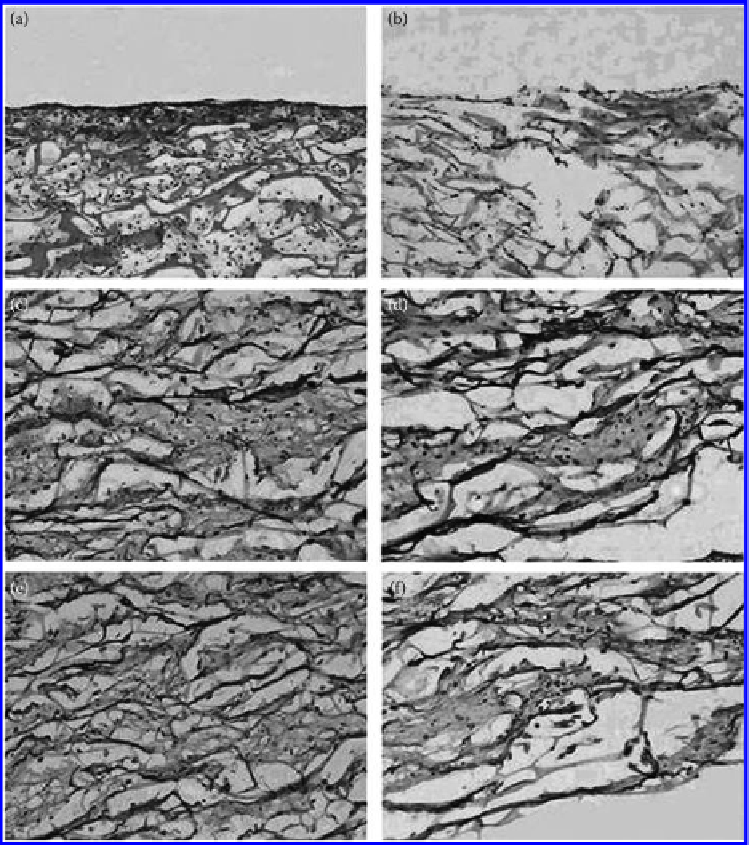
Figure 9.21
Histological (a, b) and immunohistochemical (c, f) observations of human fibroblasts cultured on the scaffolds
with (a, c, e) and without (b, d, f) bFGF-MS for 2 weeks. Images (a) and (b) were for H&E staining (×100); images
(c) and (d) were for type I collagen staining (×200); images (e) and (f) were for type III collagen staining (×200).
(From Liu, H. F. et al. 2007.
Biomacromolecules
8: 1446-1455. With permission.)
cultured for 3 weeks. During the culture process, fibroblasts can secrete ECM collagen and
growth factors to form a cell-scaffold construct, which can be defined as artificial dermis.
Then keratinocytes were also cocultured
in vitro
with fibroblasts in chitosan-gelatin
scaffolds to construct an artificial bilayer skin to construct the artificial skin. Fibroblasts
are used as the supporting layer for the primary culture of keratinocytes and they are
considered to secrete some ECM molecules to provide the physiological environment
needed for keratinocyte morphogenesis and differentiation. Meanwhile, keratinocytes can
also affect the secretion of ECMs and growth factors of fibroblasts. After 1 week of cocul-
ture in the chitosan-gelatin-HA bilayer scaffold, a thin layer of cuboid keratinocytes is
Search WWH ::

Custom Search