Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Electrochemical
workstation
CE
RE
WE
CaCl
2
NH
4
HCO
3
Chitosan
A
200 nm
H
+
D
+e
H
2
pH gradient
Cathodic deposition
B
C
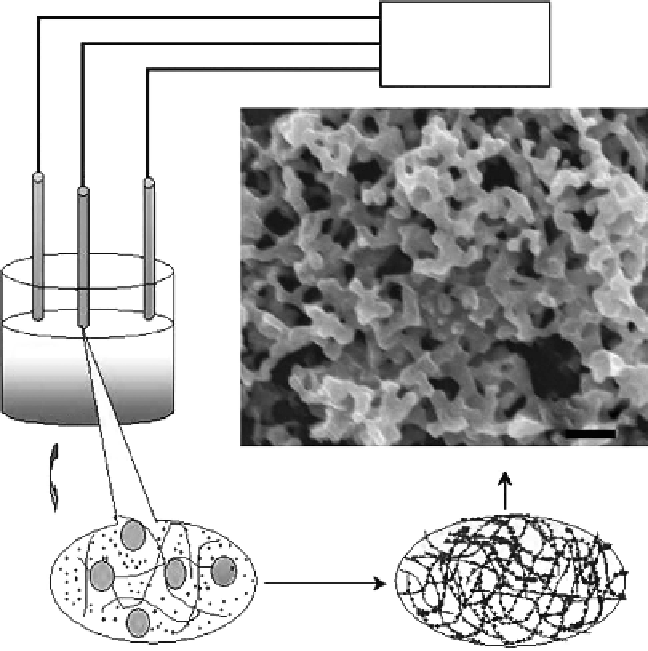
Figure 8.14
Illustration of the formation of the porous nano-CaCO
3
-chitosan composite by coelectrodeposition (A-C) and
SEM image of the nano-CaCO
3
-chitosan composite film onto GCE (D). (From Gong, J. M. et al. 2009.
Electrochem
Commun
11: 1873-1876. With permission.)
8.5.4.7.2 Chitosan-Nano-Lanthanum Phosphate Composite
Monazite, especially lanthanum phosphate, has long been known as a ceramic mate-
rial with high-temperature stability, chemical inertness/nonreactivity toward other
ceramic oxidases, and catalytic property. Nanosized NdPO
4
shows greater advantages
and novel characteristics than regular-sized particles, such as the much larger specific
surface area. These properties may provide favorable conditions for enzyme or protein
immobilization.
The direct electrochemistry of GOx immobilized on a composite matrix based on
chitosan and NdPO
4
nanoparticles underlying on GCE was achieved [152]. The pro-
posed biosensor can catalyze the reduction of dissolved oxygen, and glucose determi-
nation was achieved based on the decrease of peak currents due to the reduction of
dissolved oxygen. The proposed composite glucose biosensor can be used for the
determination of glucose in human plasma. Furthermore, an improved stability, repro-
ducibility, and efficiency in excluding the interferences of uric acid and ascorbic acid
were also obtained.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search