Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TAble 1.5
Accumulation Rate of the Same Metal Ions and Different Valences
Accumulation Rate (%)
Ions
1 h
2 h
4 h
6 h
12 h
Fe
3+
88
92
95
96
96
Fe
2+
30
32
34
36
According to conductivity, infrared spectrometry, electron spin resonance spectrometry,
and photoelectron spectrography, they assume that one Ni
2+
ion combines with O of C3
hydroxyl and N of aminos of three glucosamines to form a chitosan-Ni(II) coordination
polymer with six coordinate bonds. According to infrared spectrometry, electron spin
resonance spectrometry, and photoelectron spectrography, they assume that one La
3+
ion
combines with O of C3 hydroxyl and N of aminos of five glucosamines to form a chitosan-
Ni(II) coordination polymer with 10 coordinate bonds.
Moreover, chitosan is especially significant for absorption of transuranic elements,
actinide elements, and lanthanides. The technique for extracting uranium isotopes from
seawater by chitosan film or fiber has good prospects.
1.5.7 graft Copolymerization
There are many active groups on chitin and chitosan available for graft copolymerization,
which changes the functions of chitin and chitosan to meet some special needs. Research on
graft copolymerization began in 1979, but did not make significant progress until the 1990s.
Graft copolymerization can be carried out by the chemical method, the radiation method,
and the mechanical method, although only the chemical method and the radiation method
have been reported so far. Based on the reaction mechanism, the methods include free-
radical-induced graft copolymerization and ion-induced graft copolymerization.
CH
2
OH
CH
2
OH
O
O
O
OH
O
OH
*
*
NH
HN
Cu
2+
HN
NH
O
OH
OH
O
*
*
O
O
CH
2
OH
CH
2
OH
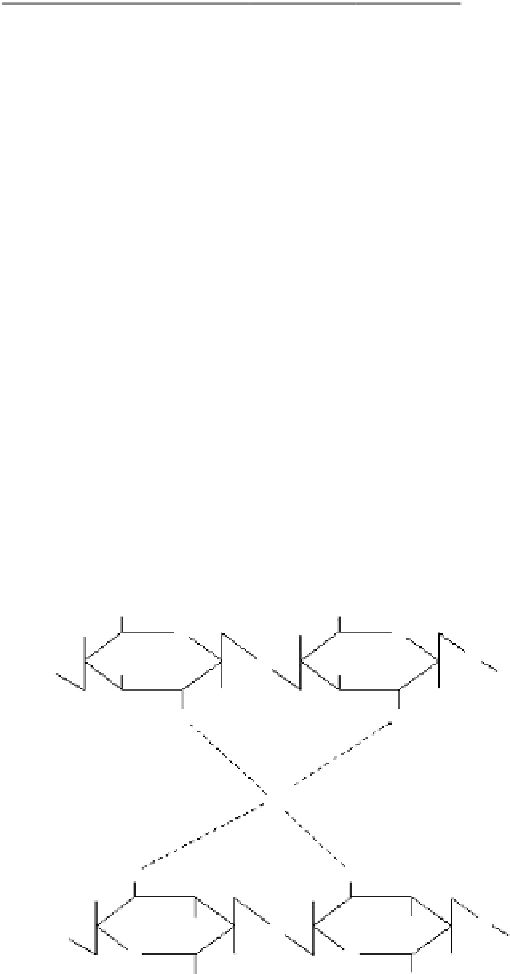
Figure 1.20
Chelation mechanism of chitosan and copper.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search