Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1. Add chitosan
drug
Evaporation of
solvent
2. Add cross-
linking agent,
stirr overnight
Dry mass
Nanogels
Reverse micelle
(surfactant dissolved
in organic solvent)
Surfactant
Surfication
Nanogels in buffer
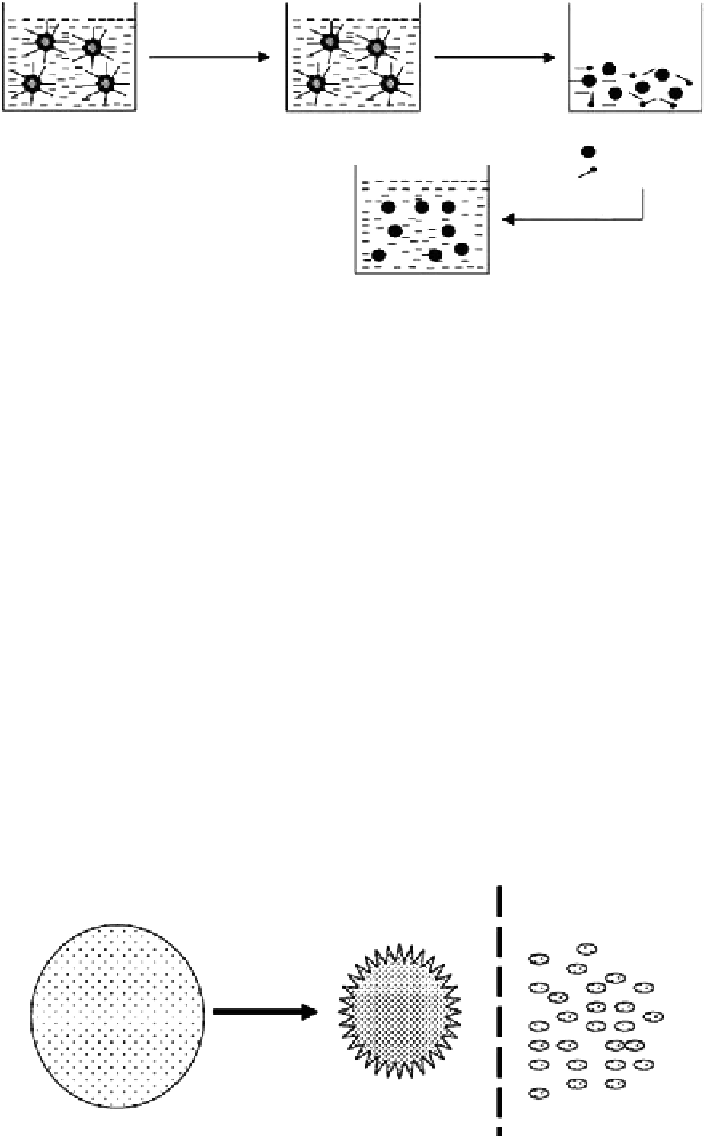
Figure 7.6
Schematic representation of the preparation of chitosan particulate systems by the reverse micellar method.
to drug and has to be determined by gradually increasing the amount of drug until the
clear microemulsion is transformed into a translucent solution. The organic solvent is then
evaporated to obtain the transparent dry mass. The material is dispersed in water and
then a suitable salt is added to precipitate the surfactant. The mixture is then subjected
to centrifugation. The supernatant solution is decanted, which contains the drug-loaded
nanoparticles. The aqueous dispersion is immediately dialyzed through a dialysis
membrane for about 1 h and the liquid is lyophilized to dry powder. The method is
schematically represented in Figure 7.6 [15].
7.2.1.7 Sieving Method [15]
In this method, microparticles are prepared by cross-linking CS to obtain a nonsticky
glassy hydrogel followed by passing through a sieve as shown in Figure 7.7 [1]. A suitable
quantity of CS is dissolved in 4% acetic acid solution to form a thick jelly mass that is cross-
linked by adding glutaraldehyde. The nonsticky cross-linked mass is passed through a
Sieve
GA
Chitosan gel
containing drug
Microparticles loaded
with drug
Cross-linked gel
Figure 7.7
Schematic representation of the preparation of chitosan particulate systems by the sieving method.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search