Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
This characteristic is an advantage in the design of DDSs. Grafting poly(N-isopropylacryl-
amide) (PNIPAAm) onto chitosan provided chitosan temperature-responsive properties
and improved the mechanical properties of its hydrogel [41]. Chung et al. [35] prepared
chitosan-g-PNIPAAm copolymer by graft polymerization of NIPAM onto chitosan using
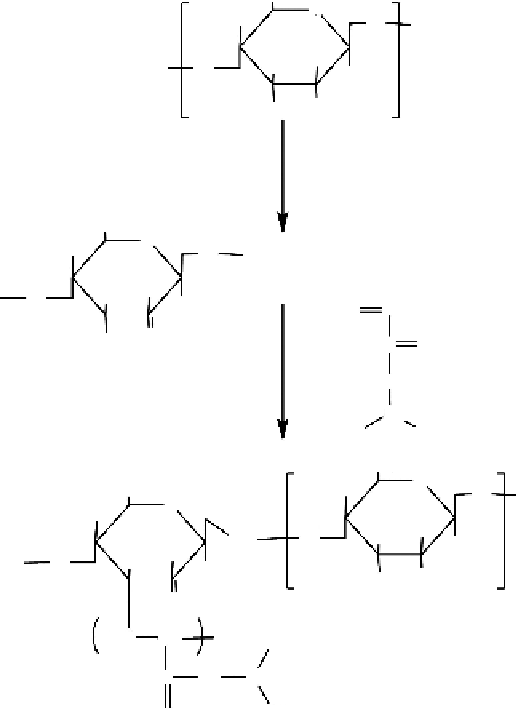
cerium ammonium nitrate as an initiator (
cf
. Figure 6.8). The efficiency and percentage of
copolymerization increased as monomer concentration increased. Similar work has been
done by Kim et al. [42] and Cai et al. [43]. Different chitosan graft copolymers with HEMA,
AA, VA, and so on can all be prepared by free radical polymerization of the monomer
using cerium ammonium nitrate as initiator [44-46]. The synthesis procedure was similar
to the above reports. Drug/chitosan-based hydrogel interaction, hydrogel properties, that
is, swelling behavior, and drug release profile greatly depended on the type of graft mol-
ecules and the grafting amount of these monomers. However, the greatest disadvantage of
this method is that the molecular weights and the molecular weight distributions of the
synthetic polymer side chain cannot be controlled as desired due to the reaction feature of
free radical polymerization.
CH
2
OH
O
H
2
H
2
Chitosan
OH
NH
2
n
Ce
4+
CH
2
OH
O
H
2
Ce
3+
+ H
+
+
H
2
OH
CH
H
2
C
NH
CO
NIPAAm
NH
CH
CH
3
H
3
C
CH
2
OH
O
H
2
CH
2
OH
O
H
2
OH
CH
2
H
2
OH
C
NH
2
n
-1
NH
2
H
2
C
CH
CH
3
C
NH
CH
CH
3
O
Figure 6.8
Schematic representation of the procedure for preparation of chitosan-g-PNIPAAm.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search