Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.0
2.0
1.5
1.5
10
10
5
5
1.0
1.0
0
0
-5
-5
0.5
0.5
-10
-10
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
μm
μm
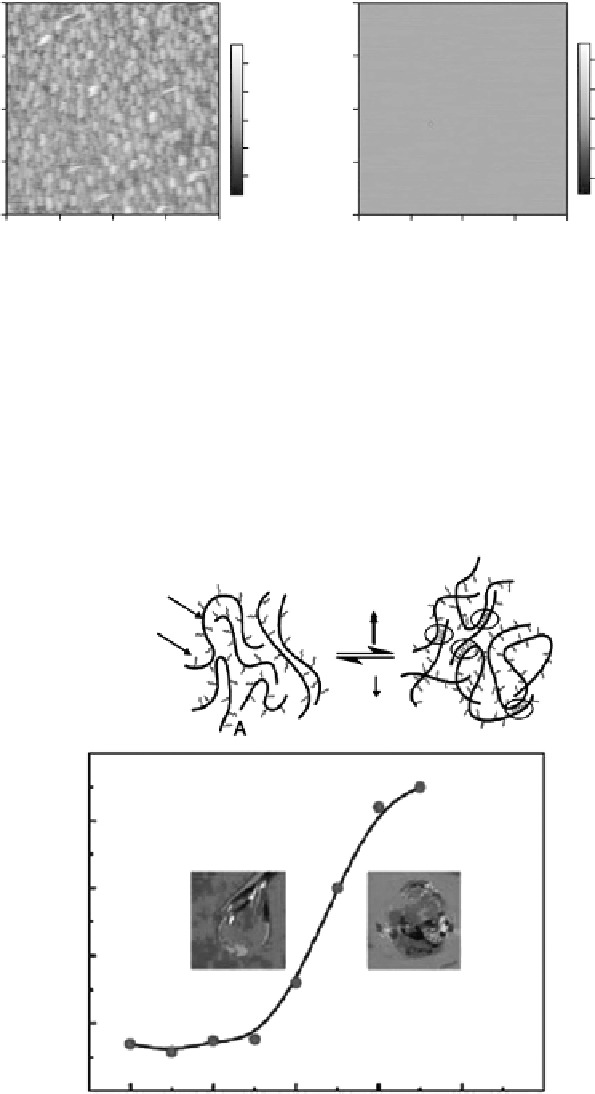
Figure 5.13
AFM topographic images of hydroxybutyl chitosan film immersed in pure water at 37°C (left) and 18°C (right).
polymer chains is disrupted, thereby rendering the graft polymer soluble in water. With
increasing temperature, both chitosan and PEG polymer chains gradually lose the attached
water molecules, the hydrophobic interactions between chitosan chains interactions start
to prevail, and a gel is formed (
cf.
Figure 5.14) [34]. In addition, the physical junction zones
of polymer chain segments increase and gel is formed. However, the high grafted rate of
Chitosan
T
PEG
T
B
A
5
4
A
B
3
2
1
0
10
20
30
Te mperature (°C)
40
50
60
Figure 5.14
Schematic representation of thermoreversible hydrogel formulation of aqueous chitosan-g-PEG solution and
the temperature dependence of viscosity of PEG-g-chitosan solution.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search