Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
H
Heparin
OX
-O
C
O
O
OH
XO
O
O
O
I
H
NH
Y
XO
O
Heparan
O
XO
-O
C
O
O
O
HO
Growth factors
O
NH
Y
XO
OX
O
G
H
Chondroitin
OX
OX
O
O
Cell surface receptors
C
O
O
O
O
XO
O
G
OX
H
NH
O
Morphogens
Dermatan
CH
2
O
-
OX OX
O
-
C
OH
O
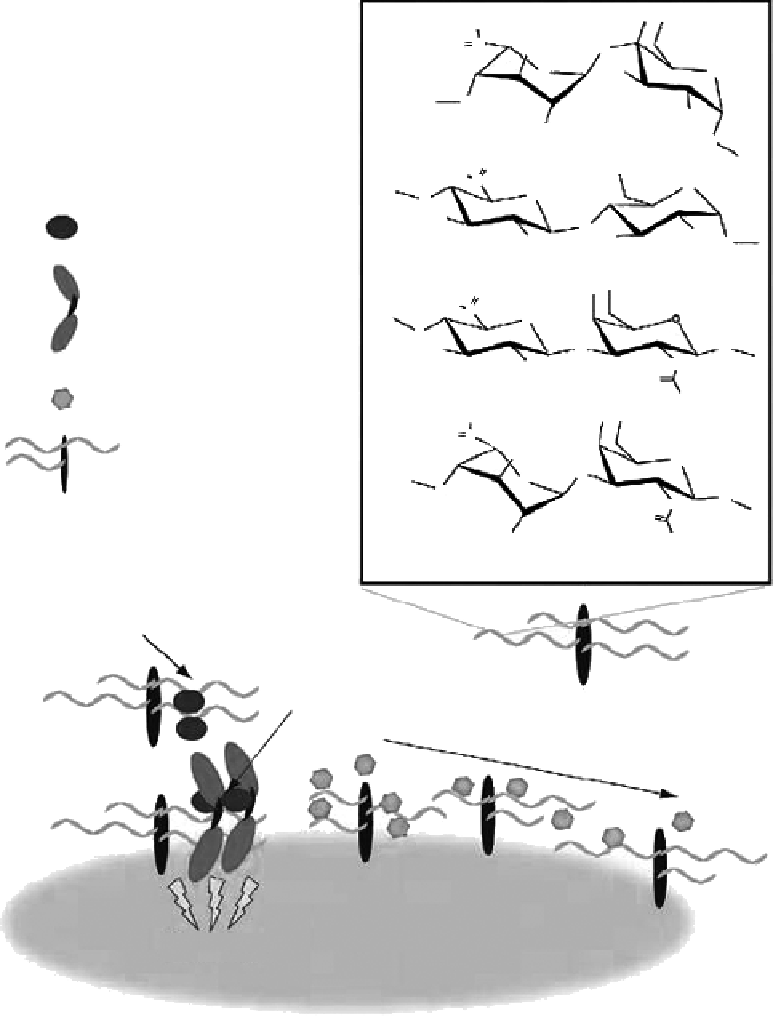
Proteoglycan (protein core
in black and GAG chains in
gray)
O
O
O
O
I
H
NH
O
XO
CH
3
X-sulfation, Y-acetylation/sulfaction
Inactive protein-protein complex
sequestered in the ECM
Active protein-protein
signaling complex
Graded affinity binding to maintain
morphogen gradients across the cell surface
Cell
Signaling
Figure 4.1
Structure and biological roles of GAGs. (From Raman, R., Sasisekharan, V., and Salisekharan, R. 2005.
Chem.
Biol
. 12: 267-277. With permission.)
A variety of natural and synthetic polymers have been used to fabricate hydrogels.
Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and its derivatives, poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and poly(hydrox-
ylethyl methacrylate), have all been used to form hydrogels with variable mechanical
strengths and biological responses. Natural polymers, such as polysaccharides and
proteins, have also been used as the structural material in hydrogels. This is largely due to
Search WWH ::

Custom Search