Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
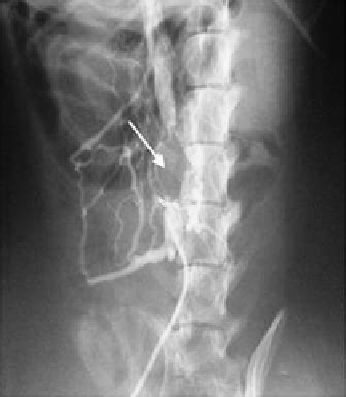
(a)
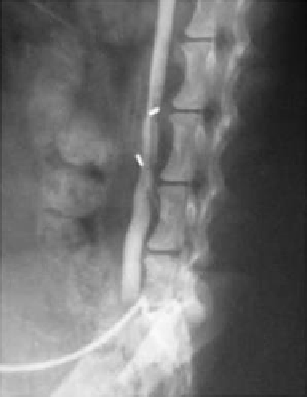
(b)
Figure 3.11
Angiograph image of vascular graft: (a) ePTFE and (b) ePTFE/CS/Hp.
3.3.1 evaluation index of Antimicrobial Activity
3.3.1.1 Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
The reference bacteria strains that represented the oral microbiota included two strict
anaerobes and two facultative anaerobic bacteria:
Porphyromonas gingivalis
(
P. gingivalis
ATCC33277),
Prevotella intermedia
(
P. intermedia
ATCC 25611),
Actinobacillus actinomycetem-
comitans
(
A. actinomycetemcomitans
Y4), and
Streptococcus mutans
(
S. mutans
Ingbritt C).
Bacterial cells were grown in BHI culture media supplemented with hemin (5 g/mL),
menadione (1%), and defibrinated goat blood (5%) before the medium was transferred
into sterilized Petri dishes at about 50°C. The agar plates were incubated in an anaerobic
chamber (Thermo, USA) with an atmosphere of 80% N
2
, 10% H
2
, and 10% CO
2
with deoxi-
dized palladium for 72 h (
P. gingivalis
,
P. intermedia
) or 48 h (
A. actinomycetemcomitans
,
S.
mutans
). A few singular colonies of each organism were picked from the blood agar plate
and diluted into sterile physiological saline. The suspension was adjusted spectrophoto-
metrically at 800 nm (OD
800
) to match a turbidity of 1.5 × 10
8
CFU mL (equivalent to 0.5
McFarland standard), and used for further antibacterial activity testing.
3.3.1.2 Test of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method was carried out
in vitro
using a
2-fold dilution technique approved by CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute)
[127]. The concentrations of the samples ranged from 5 to 0.00122 mg/mL. A serial sample
was obtained by mixing 1 mL of the standard sample with 9 mL of anaerobic medium.
A total of 100 μL of 0.5 McFarland standard organism suspension was dropped onto the
surface of the blood agar medium plate. The blood plates were incubated in the anaerobic
chamber (Thermo Life Science, USA) under an atmosphere of 80% N
2
, 10% H
2
, and 10%
CO
2
with deoxidized palladium for 72 h. Control tests were simultaneously run to ensure
reliable results. Each assessment was performed three times to ensure the reproducibility
of the experiments. MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of the tested sample at
which the bacterial colonies were not visible to the naked eye.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search