Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
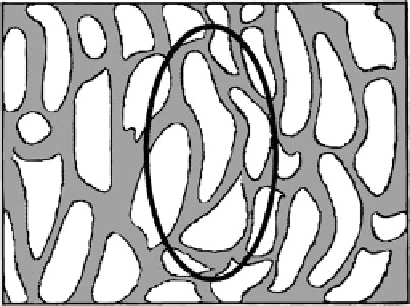
Fig. 7.7
An ellipse is
constructed by making a polar
pole of the average value
of the mean intercept length
L
(
y
) for each value of the
angle
y
. From Cowin and
Mehrabadi (
1989
)
through several values of
y
and the corresponding values of mean intercept length
L
(
) are measured, the data are often found to fit the equation for an ellipse very
closely,
y
L
2
M
11
cos
2
M
22
sin
2
ð
1
=
ðyÞÞ ¼
y þ
y þ
2
M
12
sin
y
cos
y;
(7.34)
where
M
11
,
M
22
and
M
12
are constants when the reference line from which the angle
y
is measured is constant. The subscripts 1 and 2 indicate the axes of the
x
1
,
x
2
coordinate system to which the measurements are referred. The ellipse is shown
superposed on the binary microstructure it represents in Fig.
7.7
. The mean inter-
cept lengths in all directions in a three-dimensional binary microstructure structure
would be represented by an ellipsoid and would therefore be equivalent to a positive
definite second rank tensor. The constants
M
11
,
M
22
and
M
12
introduced in the
foregoing are then the components in a matrix representing the tensor
M
which are
related to the mean intercept length
L
(
n
), where
n
is a unit vector in the direction of
the test line, by (1/
L
2
(
n
))
¼ n
∙
M
∙
n
.
The fabric tensor is commonly computed from data obtained by using stereo-
graphic or image analysis methods (Odgaard
1997
) such as Mean Intercept Length
(MIL) (Whitehouse, 1974), Volume Orientation (VO) (Odgaard et al., 1990), Star
Length Distribution (SLD) (Smit et al.
1998
), or Intercept Segment Deviation
(Chiang et al.
2006
). The experimental procedure for the fabric measurement of
cancellous bone is described by Whitehouse (1974), Harrigan and Mann (1984),
Turner and Cowin (1987) and Turner et al. (1990). A number of ways of
constructing a fabric tensor for a material with two distinct constituents are
described by Odgaard (
1997
,
2001
) for a particular porous material, cancellous
bone. These methods are applicable to any material with at least two distinct
constituents and include the stereological methods known as the mean intercept
length method, the volume orientation method and the star volume distribution
method. In multiphase materials such as cellular materials, foams, and cancellous
bone, the unit vectors may represent the orientation of the interface surface area or
Search WWH ::

Custom Search