Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
FDA
Review
Scale-up
to Mfg.
Discovery
Preclinical
Clinical Trials
5,000-10,000
leads
250
leads
5
leads
One
drug
Number of Volunteers:
20-
100
100-
500
1,000-
5,000
3 - 6 years
6 - 7 years
0.5 - 2 years
~ 25% of Total R&D Cost
~ 8%
~ 15%
~ 35%
~ 5%
~ 11%
71-
84
%
44-
56
%
64
-68%
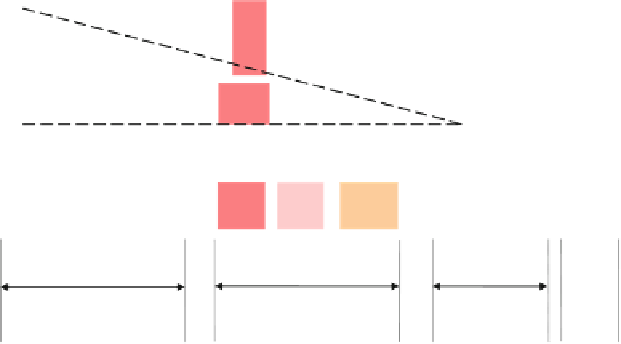
{Estimated Probabilities for Successful Completion of
Each Phase of Clinical Trials for Pharma and Biotech Firms.
The biotech firm probabilities are in
italics
.}
Fig. 2.1
The research and development process for new drugs (compiled from data in PhRMA
Pharmaceutical Industry Profi le
2011
; DiMasi and Grabowski
2007
)
2.2.3.2
Drug Development and Clinical Trials
Upon completion of drug discovery, pharmaceutical fi rms prepare for the next criti-
cal stage in the innovation process—drug development through clinical trials on
humans. Before clinical trials can begin, the researchers must fi le an
Investigational
New Drug
(
IND
) application with the FDA. As part of the submission, the drug
sponsor must provide clinical evidence in support of claims about the primary drug
indication (the targeted medical condition).
7
Drug development is structured as a linear sequence of several phases (Fig.
2.1
).
The transition to each next phase is conditional on a favorable outcome from the one
preceding it. Each phase of the clinical trials could end up with a decision to proceed,
suspend, or terminate the testing. The fi rm may decide to halt or withdraw its applica-
tion on fi nancial or commercial grounds, or choose to stop the trials in the light of
adverse new information. The FDA can mandate that the trials be terminated at any
time if problems arise. In addition, in some cases a study may be stopped because the
7
The IND application outlines the results of the preclinical work, the candidate drug's chemical
structure and how it is thought to work in the body, a listing of the expected side effects, and infor-
mation about the manufacturing process. The IND also contains a detailed test plan specifying
how, where, and by whom the clinical studies will be performed.


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search