Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
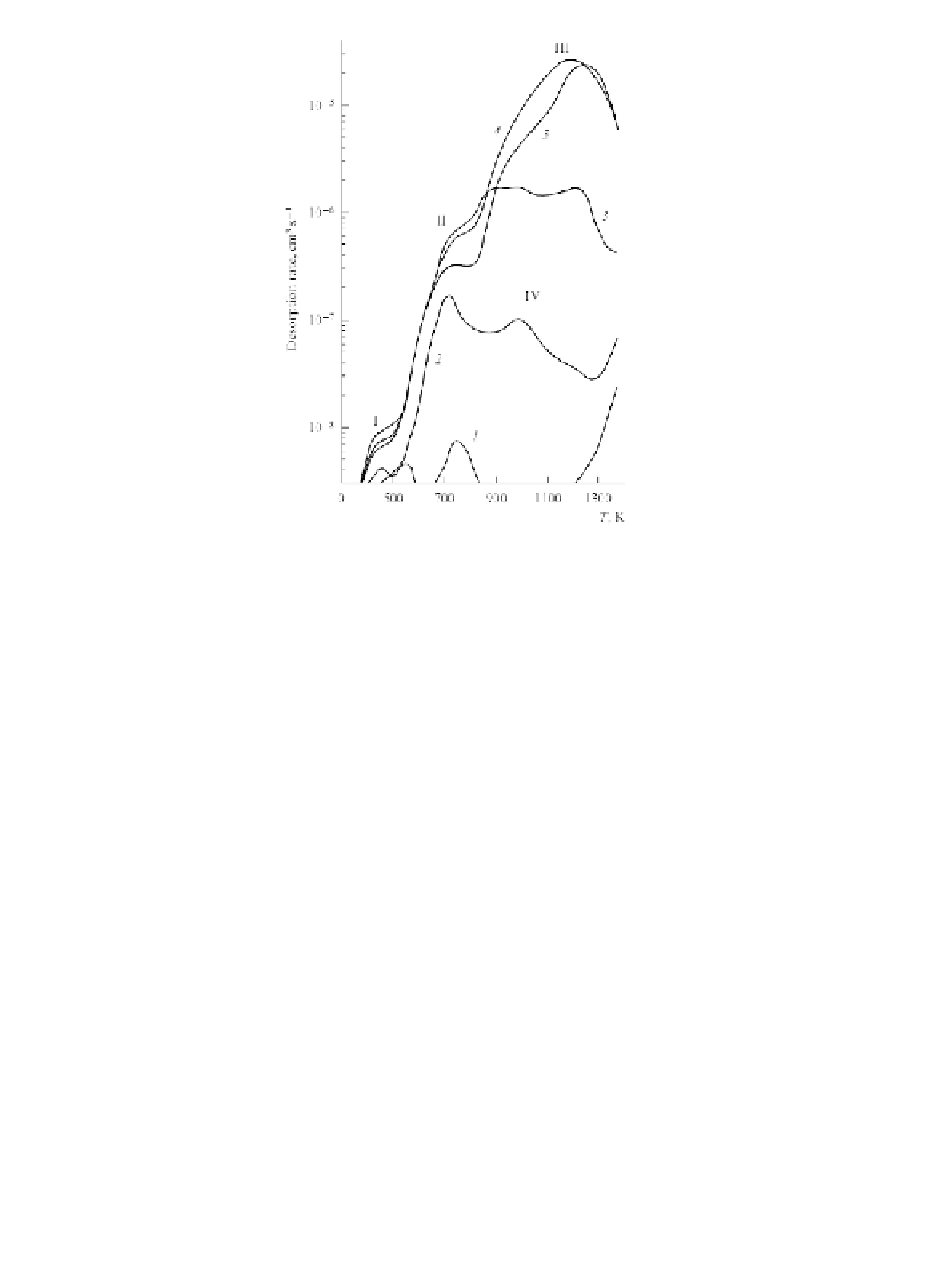
Figure 2.5
Temperature-programmed desorption curves (with TPD
peaks I-IV) for deuterium from ISO-88 isotropic graphite
hydrogen-saturated at 60 kPa (5 h) at temperatures of 473 K
(1), 673 K (2)
,
773 K (3), 973 K (4)
,
and 1173 K (5)
[5].
Taking into account the experimental data of Fig. 2.5, we can
write the mass action law for the reaction (2.4) as
X
/
X
________________________________
III
IIIm
)]
,
(2.5)
K
=
(4)III
0
1/2
(
P
/
P
)
[1 - (
X
/
X
H
III
IIIm
H
2
2
which corresponds to the Sieverts-Langmuir absorption isotherm,
i.e., the Langmuir dissociative absorption isotherm.
At small pressures (
0
K
(
P
/
P
)
1/2
<< 1), it corresponds to the
(4)III
H
2
H
2
Sieverts isotherm
1 / 2
0
1 / 2
K
(
P
/
P
)
P
X
( 4)III
H
H
H
III
2
2
K
2
,
(2.5a)
0
1 / 2
( 4)III
0
X
1 +
K
(
P
/
P
)
P
III m
( 4)III
H
H
H
2
2
2
where the equilibrium constant for reaction (2.4) is described by
D
S
D
H
( 4)III
( 4)III
K
exp
exp
(2.6)
( 4)III
R
RT