Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
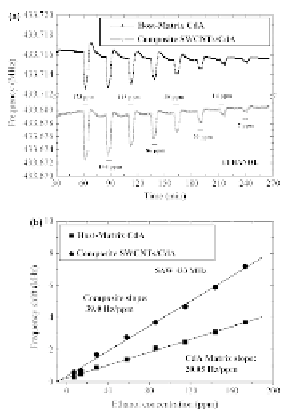
Figure 9.37
(
) Transient response of two SAW 433 MHz sensors
coated by the same thickness of nanocomposite 27.5 wt.%
SWCNT/CdA and unembedded CdA host matrix toward
various
a-Left
pulses
of
ethanol
decreasing
concentrations.
(
) Comparison of the calibration curves for the SAW 433
MHz microacoustic sensor coated with the same thickness
of nanocomposite 27.5 wt.% SWCNT/CdA and unembedded
CdA host matrix toward ethanol, at room temperature. The
coating thickness for both SAW sensors is two monolayers.
Comparison of SAW gas sensitivity toward polar and
nonpolar vapor molecules between (
b-Left
) nanocomposite
27.5 wt.% SWCNT/CdA and unembedded CdA host matrix
with the same thickness of two monolayers using a SAW 433
MHz device, and between (
a-Right
) SAW 315 and 433 MHz
microacoustic sensors using a two-monolayer thick SWCNT/
CdA 27.5 wt.% nanocomposite, at room temperature. The
concentration range of ethanol, ethylacetate, and toluene is
1-180, 1-500, and 1-150 ppm, respectively. This figure is
reprinted and adapted with permission from Elsevier [113].
b-Right
The highest sensitivity of the SAW 433 MHz sensor coated by
two monolayers of LB SWCNT 75 wt.% nanocomposite film has been
obtained for toluene as high as 145 Hz/ppm [179]. This excellent
sensitivity to toluene of the SWCNT/CdA nanocomposite results up
to more than an order of magnitude higher than the sensitivity of
the organic molecular cavities materials of
β
-cyclodextrin reported
in literature as highly sensitive coating (60 nm thick) onto SAW
433 MHz quartz devices with a sensitivity to toluene of 10 Hz/ppm.