Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
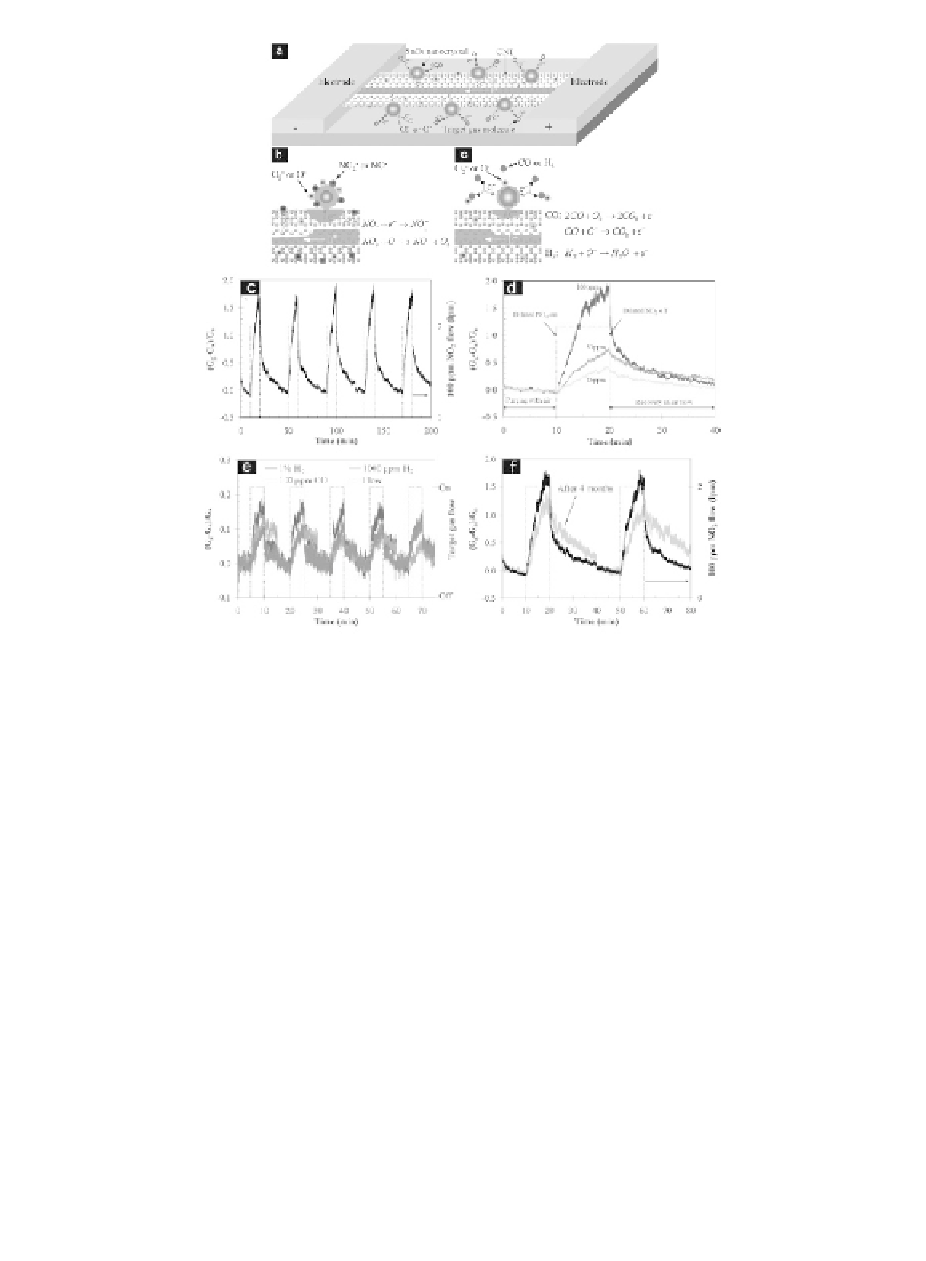
Figure 9.26
(
nanocrystals supported on an indi-
vidual CNT used as gas-sensitive platform. Possible gas sens-
ing mechanisms include (
a-Top
) Discrete SnO
2
b-Top
) direct adsorption of target
molecules (NO
/CNT surface inducing electron
transfer and changing the sensor conductivity (Mechanism
1) and (
) onto SnO
2
2
c-Top
) catalytic reaction between target gas mole-
cules (H
and CO) and oxygen adsorbates releasing electrons
back into SnO
2
/CNT surface and changing sensor conductiv-
ity (Mechanism 2). Electrical sensing performance: (
2
c-Down
)
Dynamic response of SnO
/CNT sensor for room-tempera-
ture detection of 100 ppm NO
2
. (
d-Down
) Dependence of
2
sensor response on NO
concentrations of 100, 50, and 25
2
ppm. (
e-Down
) Room-temperature responses of SnO
/CNT
2
sensor to 1% and 0.1% H
, and 100 ppm CO diluted in air.
2
(
) Comparison of sensing performance of the as-fab-
ricated SnO
f-Down
/CNT sensor with that of the same sensor after
a four-month period. The gas sensor performance degrades,
but the device is still working. This figure is reprinted and
adapted with permission from Wiley-VCH [226]. See also
Color Insert.
2