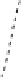Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
in the additional chemical modification of different UDD by means
of the same acid treatment, similar to the procedure of extraction
of nanodiamonds from detonation soot. The productivity of this
approach was checked using UDD samples of different types with
widely different initial surface properties.
All examined samples were subjected to the identical chemical
procedure of nanodiamond extraction, which included treatment in
concentrated mineral acids and oxidation by perchloric acid [60].
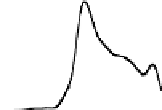
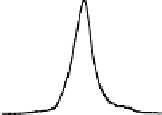
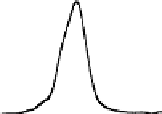
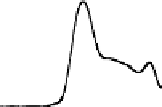
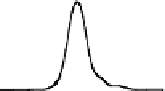
Chemical properties of functional groups on the surface of UDD were
characterized by TDMS method. It was found that chemical treatment
caused an increase in the “degree of oxidation” of surface, that was
manifested as a shift of the maxima of thermal CO desorption to lower
temperatures, as shown in Fig. 6.5 for the samples of two types, and
in an increase in the total amounts of carbon oxides desorbed in the
range of 400-700°C (twice for K-2 and five-fold for CH-7).
CO
2
CO
1
1
2
2
3
3
0
200
400
600
800
1000
0
200
400
600
800
1000
TEMPERATURE,
o
C
Figure 6.5
Effects of the modifications of UDD K-2 (solid line) and CH-7
(dashed line) on thermal desorption of CO and CO
. (1) Initial
samples; (2) after chemical treatment with acids; and (3) after
oxidation in the air at 370°C.
2
At the same time it was found that the acid treatment does not
remove completely the difference in the initial properties of the
samples. The profiles of the thermal desorption of both CO
and
CO from chemically processed samples of different types remained
2