Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Polyhedral multi-layered carbon nanostructures (the trade mark
astralene) are closed nanostructures consisting of bent graphite
layers. They are characterized by particle size of 10-150 nm,
interlayer distance of 0.336 nm and average pore size of 20-60 nm
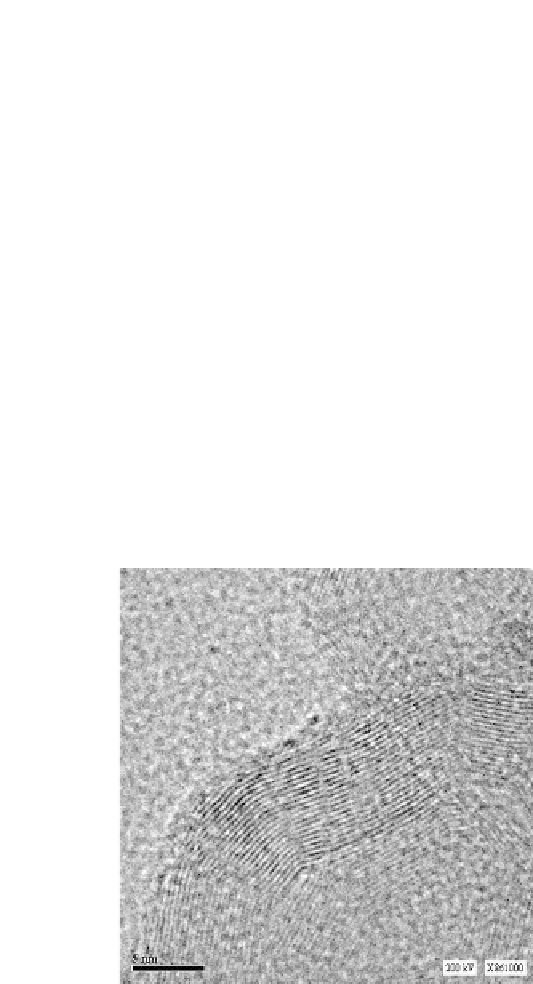
[29]. The results of recent researches presented in Ref. [39] provide
a direct proof of that the astralene particles are multi-faceted, multi-
layer structure with an hollow inside. The polyhedra facets are
constituted by a set of 20-50 flat graphite sheets. A typical image
of an astralene particle, obtained by high-resolution transmission
electron microscopy, is presented in Fig. 4.2.
Astralenes also possess a high thermal stability. They are
characterized by the existence of a cloud of delocalized
-conjugated
electrons, whose interaction with optical radiation results in the
formation of excited triplet states similar to those of fullerenes.
The set of reflections for astralene particles presented in the X-ray
diffraction spectrum (Fig. 4.1) corresponds to the most characteristic
interplanar distances of graphite-like particles of various shapes
and sizes. The only constant signal of the X-ray spectrum is a reflex,
corresponding to the d
p
interplanar distance of graphite, 3.36 Å.
001
Figure 4.2
TEM image of a typical astralene particle.
It should be noted that, due to high energy of the dispersion
interactions, astralene powders contain rather large agglomerates.