Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 8
(continued)
Horton et al.
2002
). Using force volume imaging (Quist et al.
2000
) , regional
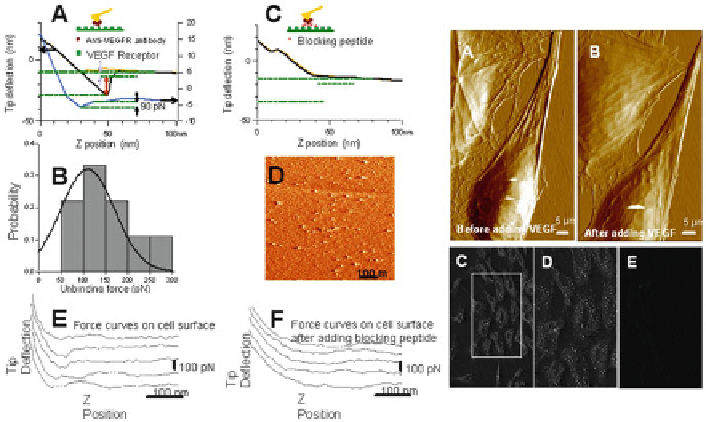
distribution as well as ligand- or antibody-induced clustering of vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) receptors are reported (Fig.
8
) (Almqvist et al.
2004
) . Unbinding
forces of 60-70 pN were observed, which could be reduced by competitive inhibi-
tion using antibodies.
Force mapping can also be useful for volume measurement on spherical cells
and/or cells weakly attached to the substrate surface. Using combined AFM with
fl uorescence microscopy, Quist et al. (
2000
) have shown volume regulation of
several cell lines through hemichannels. The added benefi t of using force mapping
is that not only is data obtained with respect to unbinding forces, but simultaneous
with imaging one can map the stiffness of the cell membrane. The stiffness is
obtained by looking at the approach force distance curves in each pixel and results
in an elasticity map. Almqvist et al. (
2004
) showed clustering of receptors using
this technique, and Quist et al. (
2000
) showed the cytoskeletal stiffness change
induced by volume change in the cell. By using antibodies conjugated on the AFM
tip by linker molecules that act on different regions of the connexin peptide that
makes up the hemichannels, epitopes that open and close the channels can be
mapped in response to variations in extracellular calcium concentration (Liu et al.
2006
). Such mapping or channel domains and how they react to different antibodies
and environmental distraction are a great help in designing drugs for ion channel-
related diseases.