Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 7
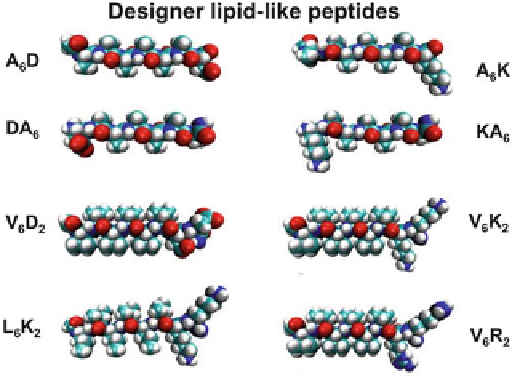
Few examples of designer lipid-like peptides. These peptides behave like lipids and surfac-
tants that can undergo self-assembly in water to form well-ordered structures. They can also stabi-
lize diverse membrane proteins and membrane protein complexes. The amino acids are one-letter
codes, the number refers to the number of amino acid residues. Color code:
red
oxygen;
blue
nitro-
gen;
teal
carbon;
white
hydrogen
Several lipid-like peptides have been designed using nature's lipid as a guide. These
peptides have a hydrophobic tail with various degrees of hydrophobicity and a
hydrophilic head; either negatively charged aspartic and glutamic acids or positively
charged lysine or histidine (Fig.
7
). These peptide monomers contain 7-8 amino
acid residues and have a hydrophilic head composed of aspartic acid and a tail of
hydrophobic amino acids, such as alanine, valine or leucine. The length of each
peptide is approximately 2 nm, similar to that of biological phospholipids (Vauthey
et al.
2002
; Santoso et al.
2002
; von Maltzahn et al.
2003
; Yang and Zhang
2006
;
Nagai et al.
2007
; Yaghmur et al.
2007
). The length can also be varied by adding
more amino acids, one at a time to a desired length as shown in Fig.
8
.
Although individually these lipid-like peptides have completely different com-
position and sequences, they share a common feature: the hydrophilic heads have
1-2 charged amino acids and the hydrophobic tails have four or more consecutive
hydrophobic amino acids. For example, A
6
D (ac-AAAAAAD), V
6
D (ac-VVVVVVD)
peptide has six hydrophobic alanine or valine residues from the N-terminus fol-
lowed by one negatively charged aspartic acid residues, thus having two negative
charges, one from the side chain and the other from the C terminus. In contrast,
V
6
K
2
(ac-VVVVVVKK) or V
6
R
2
has six valines as the hydrophobic tail followed by
two positively charged lysines or arginines as the hydrophilic head (Vauthey et al.
2002
; Santoso et al.
2002
; von Maltzahn et al.
2003
; Yang and Zhang
2006
; Nagai
et al.
2007
; Yaghmur et al.
2007
).
Since these lipid-like peptides are not directly relevant to tissue regeneration, we
will not elaborate on them further. Their applications in material sciences sprout