Robotics Reference
In-Depth Information
Instances
or
Known Cases
Knowledge
Engineer
Domain
Specialist(s)
Knowledge
Acquisition
by Rule
Inference
or
Induction
Say How
Know-How
DEVELOPMENT
PHASE
domain-specific
rules, facts,
data and assertions
Rules
and
Domain
Data
Pty
KB
Knowledge
Base
USE PHASE
Prompts
Case-Specific Data
Conclusions
Explanation
User
User
Interface
Inference
Engine
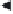
Figure 49.
A basic schema for knowledge-based applications (after “Knowledge-
Based Expert Systems,” Roger Clarke, available at
http://www.anu.edu.au/people/
knowledge (i.e., the rule-base) and the data it has been given specifically
for the particular problem being solved—this includes the data provided
by the user and the partial conclusions of the system based on this data
that have already been reached during the problem-solving process.
The system asks a question, the user provides an answer, the system
uses its
inference engine
to draw inferences from the user's answer com-
bined with one or more of its rules and, as a result of its inferences, the
system decides what question to ask next. The process is thus one in
which the system's rule-base and its inference engine co-operate, to sim-
ulate the reasoning process pursued by a human expert when analysing
a problem and arriving at a conclusion. This process continues until
the system is satisfied that it cannot improve on its current assessment,
whereupon it announces its opinion, perhaps accompanied by a measure
of how confident the system is in that opinion.
Knowledge Engineering
The role of the knowledge engineer is to acquire expertise, mainly from
human experts and sometimes from published sources. This expertise is