Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Lungs
Capillary blood
Tissue
Macrophage
Venous blood
Slowly perfused tissues
Arterial blood
Capillary blood
Tissue
Macrophage
Heart
Capillary blood
i.v.
dose
Tissue
Blood
Blood
Macrophage
Brain
Capillary blood
Tissue
Macrophage
Kidneys
Capillary blood
Tissue
Macrophage
Liver
Capillary blood
Macro-
phages
Macro-
phages
Tissue
Excreta
Macrophage
Immune organs
Capillary blood
Tissue
Macrophage
Inactive macrophages
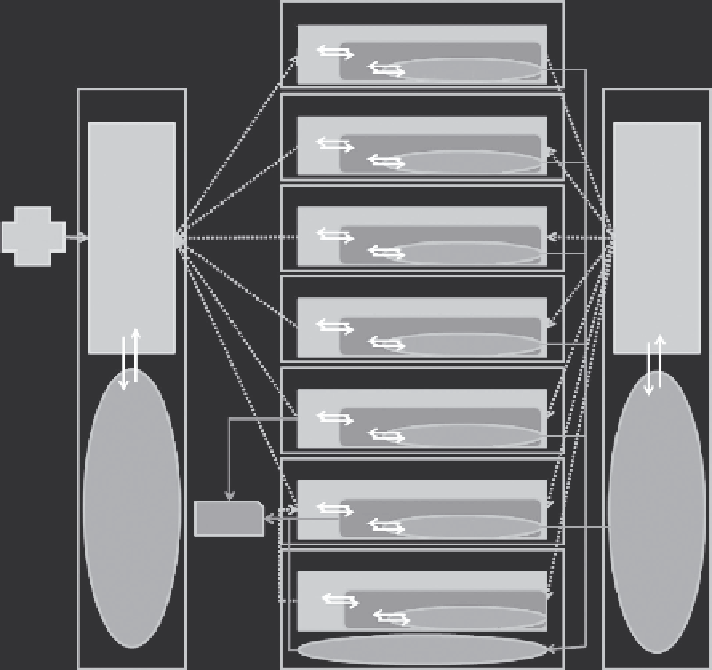
FIGURE 11.13
General framework of the PBPK model for nanoparticles. (From Li, D., Emond, C., Johanson, G.,
Jolliet, O. PBPK modeling of polyacrylamide nanoparticle biodistribution in rats.
International
Society of Exposure Science 21st Annual Meeting
, Oct 23-27, 2011, Baltimore, and
Society of
Toxicology 51st Annual Meeting
, Mar 11-15, 2012, San Francisco.)
validated an extended PBTK model that embeds macrophage subcompart-
ments within each PBTK model compartment to better reflect biodistribu-
tion and capture mechanisms (Figure 11.13). The first results from Li et al.
192
suggest that the uptake rate by macrophages will decrease by up to 20-fold
as the size of nanoparticles increases from 30 to 300 nm, while the uptake
capacity for mass increases up to 6-fold.
11.3.3.4 Ecotoxicological Impacts
Historically, the characterization modeling of freshwater ecotoxicity has
used the reciprocal of the predicted no effect concentration (PNEC) as the