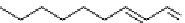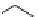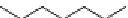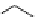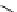Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
N
HN
+
H
O
H
2
N
N
OH
HNE
Michael addition
Guanine
O
-
O
O
O
N
N
H
+
HN
HN
H
H
H
H
OH
OH
Michael adduct (enol)
Michael adduct (keto)
Nucleophilic addition
-
O
O
OH
O
N
N
N
N
+ H
+
H
H
H
H
OH
OH
Guanine 1,
N
-2-propane adduct
FIGURE 7.22 Formation of a 1,N-2-propane adduct of guanine following
reaction of 4-hydroxynonenol (HNE) with guanine. HNE reacts with guanine
via Michael addition to form an enol adduct, which subsequently tautomerizes
and undergoes a nucleophilic addition to form a stable adduct.
protein cross-linking, ultimately damaging the cellular membrane
(Poliakov et al., 2004).
7.4.2 Oxidative Stress from Methanol Exposure
7.4.2.1 Evidence for MeOH-Initiated ROS Formation Studies have
demonstrated enhanced lipid peroxidation in brain, liver, bile, erythro-
cytes, urine as well as lymphoid organs of rats intoxicated both acutely
and chronically with MeOH (Skrzydlewska and Farbiszewski, 1997b;
Skrzydlewska et al., 1998, 2000; Dobrzynska et al., 2000; Parthasarathy
et al., 2006a,b) (Table 7.11). Following an acute exposure of rats to
MeOH, one group reported an increase in enzymatic and nonenzymatic