Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
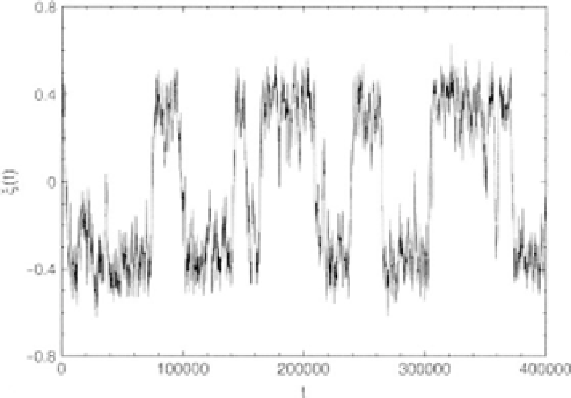
Figure 7.4.
The global variable
ξ(
t
)
as a function of time is graphed for the parameter values
K
=
1
.
05 and
g
=
0
.
01 for a web with 10
5
nodes; redrawn from [
15
] with permission.
between its two states to a condition in which all the spins are aligned and the mater-
ial is magnetized. In the social domain the phase transition is the process of reaching
consensus or agreement.
The probability density functions of the sojourn times in the states
0as
shown in Figure
7.4
are identical since the potential is symmetric. Thus, we denote them
by
ξ>
0 and
ξ<
ψ(τ)
. In the simplest case, where the coupling parameter is on the border of criti-
cality,
K
1, and the barrier between potential wells vanishes, the probability
density for the web variable at time
t
starting initially at the origin is given by
=
K
c
=
1
e
−
ξ
2
p
(ξ,
t
)
=
√
4
,
(7.28)
4
Dt
π
Dt
using a random-walk argument. The probability density of crossing the origin at time
t
is therefore given by
1
p
(
0
,
t
)
=
√
4
Dt
.
(7.29)
π
We observe that the population at the origin is composed of particles that left the ori-
gin and went back to it an arbitrarily large number of times. As a consequence, after
summing over all the possible number of zero-crossings we obtain
∞
R
(
t
)
=
0
ψ
n
(
t
).
(7.30)
n
=
t
2
−
μ
for
renewal processes. On comparing this result with (
7.29
) we find that the power-law
index is given by
The function
R
(
t
)
has been calculated and found to be proportional to 1
/
μ
=
1
.
5
.
(7.31)