Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1
0
-1
-2
-3
-2
-1
0
Log Variable
1
2
3
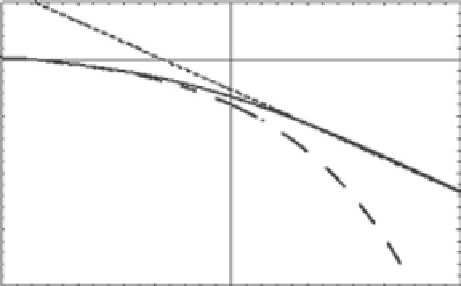
Figure 5.1.
The solid curve is the MLF, the solution to the fractional relaxation equation. The dashed curve
is the stretched exponential (Kohlrausch-Williams-Watts law) and the dotted curve is the
inverse power law (Nutting law).
fractional equations of motion that arise in a variety of contexts, emphasizing that the
inverse power law is more than curve fitting and consequently the fractional calculus
which gives rise to inverse power-law solutions may well describe the dynamics of
certain complex webs.
5.2
Some applications
5.2.1
The fractional Poisson distribution
In Section 3.3 we considered the occurrence of events as a dynamical counting process
and discussed the Poisson process as being renewal. Here we extend that discussion and
consider the fractional dynamics introduced in the previous section as describing a new
kind of renewal process. Mainardi
et al.
[
15
] refer to this as a Mittag-Leffler renewal
process because the MLF replaces the exponential in characterizing the time interval
between events. This is a reasonable extension since the MLF
)
β
∞
n
(
−
1
)
n
β
(
t
)
≡
E
−
(λ
t
=
β)
(λ
t
)
(5.50)
β
(
1
+
n
n
=
0
reduces to the exponential for
givenby(
5.50
) can therefore
be interpreted as the probability that an event has not occurred in the time interval (0
β
=
1. The function
(
t
)
,
t
).
The corresponding pdf is given by
d
(
)
dt
.
t
ψ(
t
)
≡−
(5.51)
Another quantity involving the counting process
N
(
t
)
is the probability that
k
events
occur in the closed time interval [0
,
t
],
P
(
k
;
t
)
=
Pr
[
N
(
t
)
=
k
]=
P
(
t
k
≤
t
,
t
k
+
1
>
t
).
(5.52)