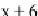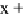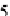Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
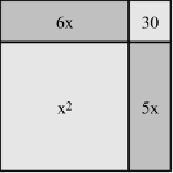
Figure 8.2
Blocks allow you to visualize the values involved in a multiplication problem.
When you work with binomial expressions, the same practice applies. You must
apply both of the terms in the first expression to both of the terms in the second
expression. A common form of binomial multiplication problem involves two
binomials that add terms:
ðx þ
6
Þðx þ
5
Þ
Binomial expressions
:
xðx þ
5
Þþ
6
ðx þ
5
Þ
Distribute the multiplications
:
x
2
þ
5
x þ
6
x þ
30
Carry out the multiplications
:
x
2
þ
11
x þ
30
Simplify
:
As Figure 8.2 illustrates, you can visualize a binomial multiplication
problem if you use a series of blocks to represent the values the multi-
plication involves.
You also commonly encounter binomial problems in which the first expression
adds terms, while the second expression subtracts one term from another. You
employ the same procedure as before. Using distribution, you multiply each term
in the second expression by each term in the first:
ð
5
m þ
4
Þðm
3
Þ
5
mðmÞ
5
mð
3
Þþ
4
ðmÞ
4
ð
3
Þ
5
m
2
15
m þ
4
m
12
5
m
2
11
m
12
In this instance, the two middle terms are of opposite signs, and whether the final
middle term is positive depends on the values of the terms combined.