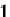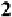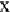Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
Multiplication and Division of Values
Addition and subtraction of terms in an equation involving inequality renders no
change in the relation of inequality. This situation changes with multiplication
and division. Specifically, it changes in instances in which you multiply and
divide by negative numbers. Why this is so relates the properties of real numbers.
As was discussed in an earlier chapter, if you multiply a negative number by a
negative number, a positive number results. Likewise, if you divide a negative
number by a negative number, a positive number results:
a a ¼ a
a
a
¼ a
The effect of such activity is that when you work with an inequality, you must
reverse the inequality sign if you divide or multiply a negative number by a
negative number. Here is an example of how this happens:
8
4
x
>
6
Original inequality
8
8
4
x
>
6
8 Remove the 8
:
No change in sign
:
4
x
>
2
Simplify
:
4
x
4
<
2
4
Divide by
4 and reverse the inequality sign
:
1
2
x
<
Simplify
:
When you divide by
4, the result of the division on the right side is a positive
value, 1/2. This changes the inequality. You must reverse sign to compensate for
this fact.
To test the validity of members of your solution set, substitute them into the
original equation. You can graph the primary solution on a number line. The
graphical representation shows that the solution is less than 1/2, so you use an
open circle.