Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
Union joins the two objects and eliminates any internal edges. Intersect finds
the volume that two solids have in common and retains that volume while delet-
ing the other portions of the objects.
This was only a brief introduction to the tools for creating and modifying sol-
ids, but it should be enough to get you started.
using Mesh-Modeling tools
In addition to the solid objects available in AutoCAD, a set of tools is available to
create mesh models. Unlike solids, meshes can't be easily manipulated and do
not have a true volume, just faces that surround an empty area. For example,
imagine this topic next to a cellophane wrapper having the same dimensions.
The topic would be a solid and the wrapper would be a mesh.
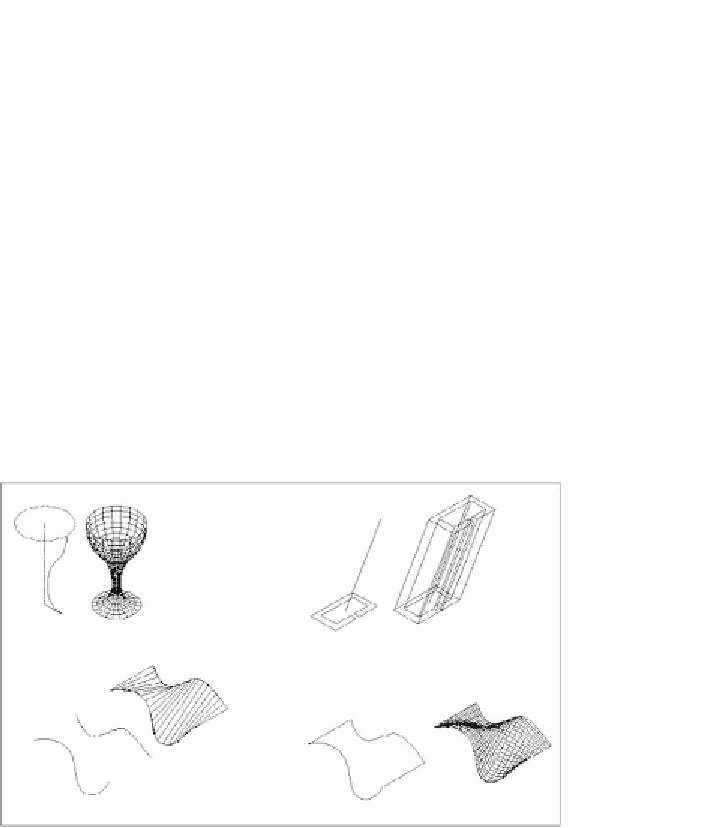
Here is a brief description of a few of the mesh tools found on the Mesh Ribbon
tab (see Figure 16.97):
Revolved mesh
Tabulated mesh
Ruled mesh
Edge mesh
FiGuRE 16.97
AutoCAD's mesh-modeling tools
Revolved Mesh
Creates a 3D surface mesh by rotating a 2D curved line around
an axis of revolution.
tabulated Mesh
Creates a 3D surface mesh by extruding a 2D object in a direc-
tion determined by the endpoints of a line, an arc, or a polyline.
Ruled Mesh
Creates a 3D surface mesh between two selected shapes.
Edge Mesh
Creates a 3D surface mesh among four lines that are connected at
their endpoints. Each line can be in 2D or 3D, and the original shape must be a
boundary of a shape that doesn't cross or conflict with itself.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search