Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
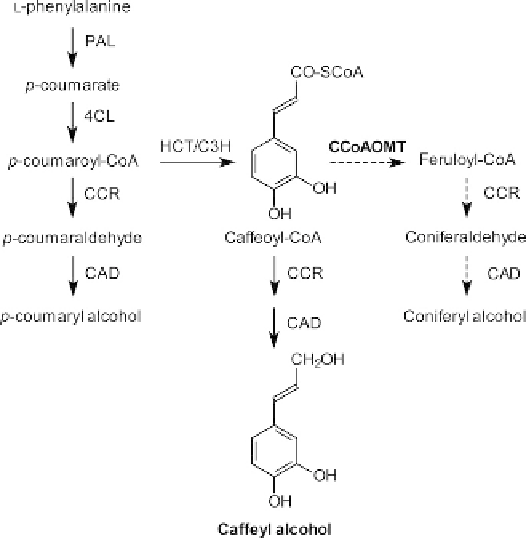
Fig. 5. Impact of CCoAOMT suppression on monolignol biosynthesis in
P. radiata. CCoAOMT suppression restricted the biosynthesis of coniferyl alcohol
(dashed arrows) and promoted the biosynthesis of caffeyl alcohol (bold). Proposed
biosynthetic pathway for the production of caffeyl alcohol in pine CCoAOMT-RNAi
lines is indicated.
into the lignin polymer (
Grabber et al.,2010
). Finally, caffeoyl-CoA has the
potential to be channelled into pathways such as flavonoid biosynthesis
(
Morreel et al.,2006
), which could have compromised the production of
caffeyl alcohol.
The incorporation of C-type units into the lignin polymer indicated a
certain level of metabolic plasticity in the lignification process in pine and
demonstrated that it is possible to incorporate non-traditional monolignols
into pine lignin. This plasticity is consistent with the existing theory that
monolignols are cross-coupled onto the growing polymer in a chemically
controlled fashion (
Ralph et al., 2004
) and that nontraditional compounds
can serve as monolignols (
Ralph and Landucci, 2010; Ralph et al., 2004,
2008b; Vanholme et al., 2008
).