Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
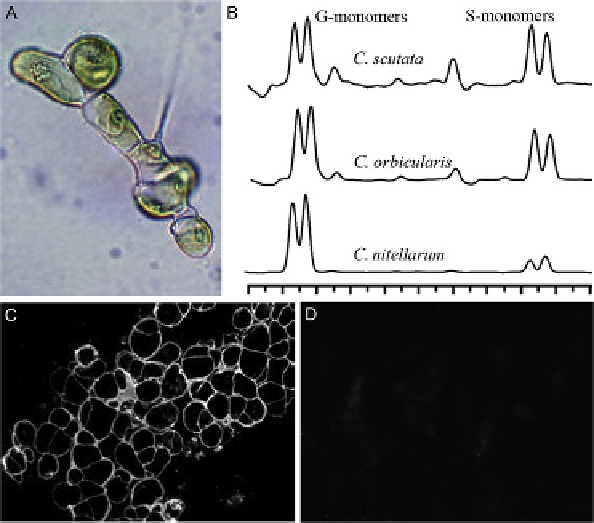
Fig. 4. Lignin-like compounds in Coleochaetales. (A) Light microscopy image of
Coleochaete nitellarum. (B) A portion of the GC-MS total ion current profile of the
monomers released by thioacidolysis of C. scutata, C. orbicularis, and C. nitellarum.
(C) Thallus of C. scutata labelled with the anti-lignin antibody anti-S/C. (D) control
immunofluorescent labelling in which primary antibody was omitted. Anti-S/C is a
polyclonal antibody against a dehydrogenative polymer (DHP) made after polymeri-
zation of a mixture of guaiacyl/syringyl 1/5 monomers, and is directed against
non-condensed
b
-O-4 GS inter-unit linkages. Adapted from
Sørensen et al. (2011)
,
reproduced with permission from Wiley-Blackwell.
between haploid and diploid generations; multicellular structures that produce
eggs and sperm and a protected embryo (
Niklas and Kutschera, 2010
).
The primary function of lignins in the first land plants is unclear and
probably was not related to structural support. Some authors point to the
fact that first functions of lignin was protection against pathogens and UV
radiation (
Boyce et al., 2003; Ligrone et al., 2008; Raven, 1984; Speck and
Vogellehner, 1988
). This hypothesis is supported by the deposition of lignin
in the cortex and not in water-conducting tissues in Early Devonian plants
like Aglaophyton, Rhynia and Asteroxylon (
Boyce et al., 2003
). Thus, cell wall
thickenings in tracheids of the first vascular plants were unlignified and only
later lignins were deposited in vascular tissues to form the modern tracheids
of extant vascular plants (
Boyce et al., 2003
). These results agree with the